Photo from wikipedia
BACKGROUND: Early renal graft dysfunction is a major problem in the early post-transplantation period and is considered a major cause of graft loss. Clinical diagnosis based on the clinical criteria… Click to show full abstract
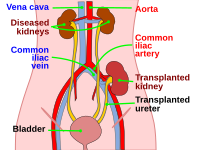
BACKGROUND: Early renal graft dysfunction is a major problem in the early post-transplantation period and is considered a major cause of graft loss. Clinical diagnosis based on the clinical criteria alone is unreliable; therefore, biopsy remains the gold standard to differentiate between rejection and non-rejection causes. AIM: This study was designed to identify and differentiate between causes of early graft dysfunction during the first post-transplantation month and to correlate between histological lesions and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for accurate diagnosis and a better outcome. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 163 renal allograft biopsies, performed in the first post-transplantation month over 6 years, were included in the study. New sections were prepared from the paraffin blocks and stained with conventional stains. Additional sections were prepared and treated by complement fragment 4d (C4d) and cluster differentiation 3 (CD3) antibodies for IHC evaluation. RESULTS: All the studied cases were from living donors. The mean patient age was 39 years with predominant males. The clinical indication for most biopsies (94.5%) was impaired graft function. Acute rejection (AR) was the main diagnostic category observed in (98/163, 60.1%); out of which, T cell-mediated rejection (TCMR) was observed in (62/98, 63.2%). Drug toxicity was suspected in (53/163, 32.5%), acute tubular injury (ATI) not otherwise specified (nos) in (21/163, 12.9%), and other lesions including thrombotic microangiopathy were observed in the remaining biopsies. The most common cause of graft dysfunction in the 1 and 2 weeks was AR representing. A significant correlation was seen between mild glomerulitis (g1) and mild peritubular capillaritis (PTC) 1, on the one side, and negative C4d staining, on the other side. No significant correlation was seen between moderate glomerulitis (g2) and moderate ptc2 at one side and positive C4d staining at the other side reflecting the poor association between the microvascular inflammation (“g” and “ptc” scores) and C4d positivity (r = 0.2). Missed mild tubulitis (t1) was found in a single case and missed moderate tubulitis (t2) was found in a single case detected by CD3 IHC. CONCLUSION: AR and drug toxicity account for the majority of early graft dysfunction, however, other pathological lesions, per se or coincide with them may be the cause. The significance of g2 per se as a marker for diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection requires further study. Considering C4d score 1 (by IHC) positive; also requires further study with follow-up. Edited by: Sinisa Stojanoski Citation: Muhammad MEE, Fadda SAA, Gabal SM, Shaker AM, Mohamad WM. Evaluation of Early Renal Allograft Dysfunction from Living Donors among Egyptian Patients (Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study). Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2021 May 07; 9(A):328-335. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2021.6081
Journal Title: Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!