Photo from wikipedia
A 34-year-old woman at 25 weeks 3 days was diagnosed with preterm labor and underwent an emergency cesarean section. The neonate did not cry or show any activity. The heart… Click to show full abstract
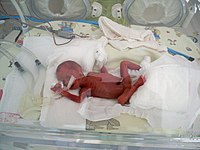
A 34-year-old woman at 25 weeks 3 days was diagnosed with preterm labor and underwent an emergency cesarean section. The neonate did not cry or show any activity. The heart rate was 80 beats/min and the oxygen saturation on pulse oximetry (SpO2) was 77%. Immediately, positive pressure ventilation was delivered by T piece resuscitator, and then anesthesiologist performed endotracheal intubation. The neonate demonstrated severe cyanosis and the SpO2 dropped to 30%. Ventilation was not successful even after intubation, and we found neck crepitus, chest wall distension, and severe cyanosis on physical examination. We suspected tension pneumothorax and performed needle thoracentesis. The neonate was stabilized and transferred to the neonatal intensive care unit for further treatment, but expired on the 10th day of life. We report a case of pulmonary air leak developing tension pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema in an extremely-low-birth-weight preterm infant immediately after birth.
Journal Title: Korean Journal of Anesthesiology
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!