Photo from wikipedia
Due to their intense electrical activity, neurons have high energy demands. This requirement makes them particularly sensitive to mitochondrial dysfunction. Like all eukaryotic cells, neurons have intrinsic mechanisms to mitigate… Click to show full abstract
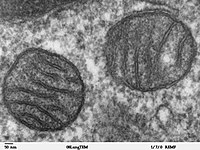
Due to their intense electrical activity, neurons have high energy demands. This requirement makes them particularly sensitive to mitochondrial dysfunction. Like all eukaryotic cells, neurons have intrinsic mechanisms to mitigate the impact of mitochondrial dysfunction and its consequent production of toxic substances. Among such (neuro)protective mechanisms, mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy) is responsible for the removal of dysfunctional mitochondria. Pathological inhibition of mitophagy, together with insufficient mitochondrial activity, results in a shortage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Simmons et al., 2020). These alterations may trigger extensive apoptotic neuronal death (Figure 1A) which, together with the post-mitotic nature of neurons, impedes the replacement of the apoptotic cells. This irreversible loss of neurons may underlie the progressive decline in the function of the central nervous system, culminating in the arousal of neurodegenerative diseases (Simmons et al., 2020). The actual role of mitochondrial dysfunction has been increasingly demonstrated in Alzheimer ’s disease. For example, post-mortem analysis of patient brains has revealed the reduced expression and activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes (Troutwine et al., 2022).
Journal Title: Neural Regeneration Research
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!