Photo from wikipedia
Context: Cyclosporiasis is an emerging enteric coccidian parasitic disease worldwide, caused by the parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis. There is scanty data from India, especially among immunocompetent patients. Aims: The aim is… Click to show full abstract
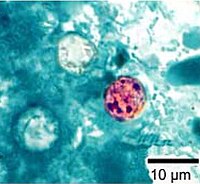
Context: Cyclosporiasis is an emerging enteric coccidian parasitic disease worldwide, caused by the parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis. There is scanty data from India, especially among immunocompetent patients. Aims: The aim is to evaluate the occurrence of Cyclosporiasis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Settings and Design: It is a prospective cohort study conducted from June 2006 to May 2018 at our tertiary care center. Materials and Methods: Stool samples were collected from the 900 patients with diarrhea (both immunocompetent and immunocompromised) and 170 healthy controls to look for Cyclospora by modified Kinyoun staining. Statistical Analysis: Mann–Whitney U test/Fisher exact test were used for statistical analysis. Results: Oocysts of C. cayetanensis were detected in 10/900 patients and none of the healthy controls. The median age of patients was 38.5 years (10-65 years) and males (6/10) outnumbered the females in harboring the parasite. Eight patients were immunocompromised (five postrenal transplant cases and one-one patient each with HIV, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and juvenile polyarthritis), and two patients were immunocompetent. Cyclospora infection was more common in immunocompromised patients (8/300, 2.67%) than the immunocompetent patients (2/600, 0.33%); P < 0.001. Eight patients responded well to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, one died, and one was lost to follow-up. Coinfection with Cryptosporidium spp. was seen in one patient. Conclusion: Cyclospora causes diarrhea in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent persons. Its burden may be underestimated due to a lack of awareness and appropriate diagnostic methods. Special staining techniques are important for diagnosis as they may be missed by routine microscopy.
Journal Title: Tropical Parasitology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!