Photo from wikipedia
A series of nanoporous carbons (NPC) Fe-C/N-900 and C/N-900 have been synthesized from one-step carbonization of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin-Fe (Fe-TCPP) and TCPP, respectively and employed as photocatalyst for the degradation of organic… Click to show full abstract
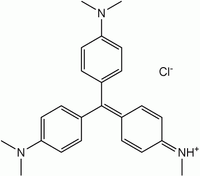
A series of nanoporous carbons (NPC) Fe-C/N-900 and C/N-900 have been synthesized from one-step carbonization of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin-Fe (Fe-TCPP) and TCPP, respectively and employed as photocatalyst for the degradation of organic dye methyl violet (MV) under UV irradiation. The optimized Fe-C/N-900 (carbonized at 900 oC for 2 h) exhibited an optimal performance in MV degradation. The photodegradation capacity of Fe-C/N-900 has been observed to be higher than that of C/N-900. The photodegradation ability of Fe-C/N-900 as a function of initial MV concentration, catalysis dosage, and pH has been also investigated. The Fe-C/N-900 material showed no apparent loss in MV degradation after four cycles. These features reveal that Fe-C/N-900 may be a promising degradant for dyes removal from water. KEY WORDS: Photocatalysis, Nanoporous carbons, Methyl violet, carbonization Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2020, 34(2), 277-284 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4314/bcse.v34i2.6
Journal Title: Bulletin of The Chemical Society of Ethiopia
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!