Photo from wikipedia
Objective: The aims of the study were (1) to compare outcomes in terms of malunited distal radius bone union in open-wedge corrective osteotomy using autogenous or allogenic bone and (2)… Click to show full abstract
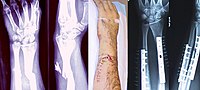
Objective: The aims of the study were (1) to compare outcomes in terms of malunited distal radius bone union in open-wedge corrective osteotomy using autogenous or allogenic bone and (2) to introduce a new parameter that quantifies the rate of the bone union. Methods: This retrospective study included 22 patients (14 males, 8 females) who underwent open-wedge corrective osteotomy with bone grafting for a malunited distal radius fracture between January 2006 and December 2018 were enrolled. The mean follow-up duration was 57.2 weeks (SD 46.1, range 12-206). All the patients were then divided into 1 of the 2 groups based on the graft material used: autogenous bone graft group (n = 10, 5 males and 5 females) and allogenic bone graft group (n = 12, 9 males and 3 females). We introduced the “duration of union/correction gap ratio” to represent the healing potential of each graft materials. Radiologic parameters including initial correction gap, radial inclination, radial length, palmar tilt, and ulnar variance were also measured pre- and postoperatively. Functional outcomes were assessed by grip strength, range of motion, and the disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand score. Results: Of the 22 patients, 16 (72.7%) achieved complete union within 12 weeks, 3 (13.6%) in over 12 weeks, and the other 3 (13.6%) showed nonunion. Excluding the 3 nonunion cases, the mean union duration was 10.6 weeks, and the mean correction gap was 10 mm. The mean correction gap was wider in the autogenous bone graft group, and the mean union duration was longer in the allogenic bone graft group. Autogenous bone grafts had a significantly lower duration of bone union/correction gap ratio than allogenic bone grafts (0.76 vs. 1.61, P < 0.001). According to the correction method (simple open-wedge corrective osteotomy vs. open-wedge corrective osteotomy OWCO), only duration of bone union/correction gap ratio reflected the actual difference between values. Conclusion: Despite autogenous bone graft donor site morbidities, in our study, autogenous bone showed better bone healing potential than allogenic bone. In terms of bone union, autogenous bone has the benefit of better union in larger gaps than allogenic bone. Surgeons can take advantage of the newly introduced “duration of bone union/correction gap ratio” to compare the bone healing potential by graft materials or surgical options. Level of Evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic Study
Journal Title: Acta Orthopaedica et Traumatologica Turcica
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!