Photo from wikipedia
In the past half century, humanity has experienced two devastating pandemics; the HIV-1 pandemic and the recent pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2. Both emerged as zoonotic pathogens. Interestingly, SARS-CoV-2 has rapidly… Click to show full abstract
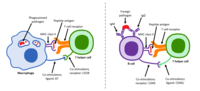
In the past half century, humanity has experienced two devastating pandemics; the HIV-1 pandemic and the recent pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2. Both emerged as zoonotic pathogens. Interestingly, SARS-CoV-2 has rapidly migrated all over the world in less than two years, much as HIV-1 did almost 40 years ago. Despite these two RNA viruses being different in their mode of transmission as well as the symptoms they generate, recent evidence suggests that they cause similar immune responses. In this mini review, we compare the molecular basis for CD4+ T cell lymphopenia and other effects on the immune system induced by SARS-CoV-2 and HIV-1 infections. We considered features of the host immune response that are shared with HIV-1 and could account for the lymphopenia and other immune effects observed in COVID-19. The information provided herein, may cast the virus-induced lymphopenia and cytokine storm associated with the acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis in a different light for further research on host immune responses. It can also provide opportunities for the identification of novel therapeutic targets for COVID-19. Furthermore, we provide some basic information to enable a comparative framework for considering the overlapping sets of immune responses caused by HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2.
Journal Title: International Journal of Medical Sciences
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!