
Bloom termination of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella: Vertical migration behavior, sediment infiltration, and benthic cyst yield
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Limnology and Oceanography"
DOI: 10.1002/lno.10664
Abstract: Abstract New resting cyst production is crucial for the survival of many microbial eukaryotes including phytoplankton that cause harmful algal blooms. Production in situ has previously been estimated through sediment trap deployments, but here was… read more here.
Keywords: bloom; sediment infiltration; cyst; alexandrium catenella ... See more keywords

Spatiotemporal genetic structure of regional-scale Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellate blooms explained by extensive dispersal and environmental selection.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Harmful algae"
DOI: 10.1016/j.hal.2019.03.013
Abstract: Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) caused by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella is a well-known global syndrome that negatively impacts human health and fishery economies. Understanding the population dynamics and ecology of this species is thus important… read more here.
Keywords: spatiotemporal genetic; alexandrium; alexandrium catenella; structure ... See more keywords
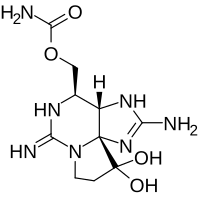
Unraveling the molecular mechanism of the response to changing ambient phosphorus in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella with quantitative proteomics.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of proteomics"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.11.004
Abstract: Phosphorus (P) is a key macronutrient limiting cell growth and bloom formation of marine dinoflagellates. Physiological responses to changing ambient P have been investigated in dinoflagellates; however, the molecular mechanisms behind these responses remain limited.… read more here.
Keywords: catenella; phosphorus; dinoflagellate alexandrium; alexandrium catenella ... See more keywords

In silico prediction of the secretome from the invasive neurotoxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Environmental microbiology reports"
DOI: 10.1111/1758-2229.12764
Abstract: Alexandrium catenella, a marine dinoflagellate responsible for harmful algal blooms (HABs), proliferates with greater frequency, distribution and intensity, in disturbed marine coastal ecosystems. The proteins secreted into seawater may play a crucial role in maintaining… read more here.
Keywords: marine dinoflagellate; alexandrium catenella; catenella;

Cloning, sequencing and transcriptional analysis of ubiquitin gene from Alexandrium catenella under different nutrient conditions
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Pakistan Journal of Botany"
DOI: 10.30848/pjb2021-2(19)
Abstract: Ubiquitin is a small conserved protein ubiquitous in all eukaryotic organisms. It plays a critical role in intracellular protein turnover, being the “tag” that marks proteins for proteolysis. Beside proteolysis, it plays vital role in… read more here.
Keywords: catenella; analysis ubiquitin; alexandrium catenella; gene ... See more keywords

Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Toxins"
DOI: 10.3390/toxins12070442
Abstract: Paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) produced by Alexandrium catenella (formerly A. tamarense) in Korean coastal waters caused the deaths of four people (in 1986 and 1996) who consumed contaminated mussels (Mytilus edulis). This led to more… read more here.
Keywords: shellfish toxins; catenella; geoje coast; alexandrium catenella ... See more keywords

Latitudinal Variation in the Toxicity and Sexual Compatibility of Alexandrium catenella Strains from Southern Chile.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Toxins"
DOI: 10.3390/toxins13120900
Abstract: The bloom-forming toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella was first detected in southern Chile (39.5-55° S) 50 years ago and is responsible for most of the area's cases of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). Given the complex life… read more here.
Keywords: alexandrium catenella; southern chile; toxicity; catenella ... See more keywords

Effects of Two Toxin-Producing Harmful Algae, Alexandrium catenella and Dinophysis acuminata (Dinophyceae), on Activity and Mortality of Larval Shellfish
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Toxins"
DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050335
Abstract: Harmful algal bloom (HAB) species Alexandrium catenella and Dinophysis acuminata are associated with paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) in humans, respectively. While PSP and DSP have been studied extensively, less is… read more here.
Keywords: acuminata; mortality; alexandrium catenella; activity mortality ... See more keywords