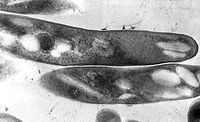
Effect of amikacin on cell wall glycopeptidolipid synthesis in Mycobacterium abscessus
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1007/s12275-017-6503-7
Abstract: Cultivation of the smooth colony Mycobacterium abscessus at the sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of amikacin changed its growth pattern including its colony morphology (smooth to rough) and cell arrangement (dispersed to cord formation). In addition,… read more here.
Keywords: cell wall; amikacin; abscessus; mycobacterium abscessus ... See more keywords

Higher versus standard amikacin single dose in emergency department patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: a randomised controlled trial.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "International journal of antimicrobial agents"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.11.009
Abstract: Recent studies suggest that intensive care unit patients treated with amikacin frequently do not attain the desired pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) target, i.e. peak amikacin concentration (Cpeak) to minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ratio of ≥8, when a… read more here.
Keywords: sepsis septic; severe sepsis; septic shock; target ... See more keywords

Efficacy of Zidovudine-Amikacin Combination Therapy In Vitro and in a Rat Tissue Cage Infection Model against Amikacin-Resistant, Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriales
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Microbiology Spectrum"
DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.04843-22
Abstract: Our study revealed for the first time that the zidovudine-amikacin combination shows a significant bactericidal effect against amikacin-resistant MDR, XDR, and PDR Enterobacteriales. Second, using in vitro and in vivo approaches, our study showed that… read more here.
Keywords: amikacin combination; amikacin; zidovudine amikacin; amikacin resistant ... See more keywords

Protective effect of ethyl pyruvate on amikacin-induced ototoxicity in rats.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "European review for medical and pharmacological sciences"
DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202204_28480
Abstract: OBJECTIVE Amikacin (AMK) is a widely used antibiotic, but its ototoxic side effects limit its use. This study investigated the effects of ethyl pyruvate (EP), known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, against AMK ototoxicity.… read more here.
Keywords: amikacin; ethyl pyruvate; group; ototoxicity ... See more keywords

FoxO3a plays a key role in the protective effects of pomegranate peel extract against amikacin-induced ototoxicity
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "International Journal of Molecular Medicine"
DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3003
Abstract: The use of amikacin (AMK) in present treatment strategies results in severe ototoxicity; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms of this toxicity remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of orally administered pomegranate peel… read more here.
Keywords: peel extract; induced ototoxicity; ototoxicity; pomegranate peel ... See more keywords