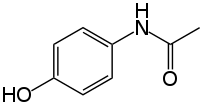
Irbesartan mitigates acute liver injury, oxidative stress, and apoptosis induced by acetaminophen in mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology"
DOI: 10.1002/jbt.22447
Abstract: Hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (APAP)‐overdose is a major concern in clinical practice. In the present work, the detoxifying effect of irbesartan (Irb) on the APAP‐induced acute liver injury was evaluated in mice. Induction of acute… read more here.
Keywords: liver injury; stress; acute liver; apap induced ... See more keywords

Naringin alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by activating Nrf2 via CHAC2 upregulation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Environmental toxicology"
DOI: 10.1002/tox.23487
Abstract: Severe acetaminophen (APAP)-induced hepatic damage is the second most common cause for hepatic transplantation. Clinically, hepatic damage caused by APAP is treated using N-acetyl-L-cysteine, which can induce numerous side effects. Naringin, a bioflavonoid abundant in… read more here.
Keywords: naringin; apap induced; liver injury; induced acute ... See more keywords

Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 2 deficiency is resistant to acetaminophen-induced liver injury
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Archives of Toxicology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02543-1
Abstract: Acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury is the main cause of acute liver failure. This study investigated the role of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 2 (mPGES-2), discovered as one of the prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthases, in mediating… read more here.
Keywords: prostaglandin; induced liver; apap induced; liver injury ... See more keywords

Polyphenols reported to shift APAP-induced changes in MAPK signaling and toxicity outcomes.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Chemico-biological interactions"
DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.09.007
Abstract: Due to its widespread availability, acetaminophen (APAP) is the leading cause for drug-induced liver injury in many countries including United States and United Kingdom. When used as recommended, APAP is relatively safe. However, in overdose… read more here.
Keywords: induced changes; toxicity; mapk signaling; apap ... See more keywords

Protective role of p53 in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Free Radical Biology and Medicine"
DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.02.028
Abstract: Abstract p53 is a tumor suppressor with a pro‐death role in many conditions. However, in some contexts, evidence supports a pro‐survival function. p53 has been shown to be activated in acetaminophen (APAP) toxicity but the… read more here.
Keywords: role; apap induced; liver injury; p53 ... See more keywords

20(R)‐ginsenoside Rg3, a rare saponin from red ginseng, ameliorates acetaminophen‐induced hepatotoxicity by suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway‐mediated inflammation and apoptosis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "International Immunopharmacology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.030
Abstract: ABSTRACT Although ginsenoside Rg3 was isolated as a major component of Korea red ginseng and confirmed to exert potential hepatoprotective effect on acetaminophen (APAP)‐induced liver injury via induction of glutathione S‐transferase (GST) in vitro, thein… read more here.
Keywords: apoptosis; pi3k akt; rg3; apap induced ... See more keywords

Hesperetin attenuated acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting hepatocyte necrosis and apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response via upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "International immunopharmacology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106435
Abstract: Acetaminophen (APAP) is a common antipyretic and analgesic drug, but its overdose can induce acute liver failure with lack of effective therapies. Hesperetin, a dihydrogen flavonoid compound, has been revealed to exert multiple pharmacological activities.… read more here.
Keywords: apoptosis; inflammatory response; apap induced; hesperetin ... See more keywords

Pterostilbene-Loaded Soluplus/Poloxamer 188 Mixed Micelles for Protection against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Molecular pharmaceutics"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00881
Abstract: Excessive acetaminophen (APAP) induces excess reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to liver damage. Pterostilbene (PTE) has excellent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, but poor solubility limits its biological activity. In this study, we prepared PTE-loaded Soluplus/poloxamer… read more here.
Keywords: liver injury; soluplus poloxamer; poloxamer 188; apap induced ... See more keywords

Phenelzine protects against acetaminophen induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Drug and chemical toxicology"
DOI: 10.1080/01480545.2023.2217696
Abstract: Acetaminophen (APAP) overdosing is the most common cause of drug-induced liver failure. Despite extensive study, N-acetylcysteine is currently the only antidote utilized for treatment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect and… read more here.
Keywords: effect; apap; phenelzine protects; apap induced ... See more keywords

The complex roles of neutrophils in APAP‐induced liver injury
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Cell Proliferation"
DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13040
Abstract: Acetaminophen (APAP) is a widely applied drug for the alleviation of pain and fever, which is also a dose‐depedent toxin. APAP‐induced acute liver injury has become one of the primary causes of liver failure which… read more here.
Keywords: induced liver; roles neutrophils; apap induced; liver injury ... See more keywords

Gut Microbiota Mediates the Therapeutic Effect of Monoclonal Anti-TLR4 Antibody on Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Microbiology Spectrum"
DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00647-22
Abstract: In this study, we found the monoclonal anti-Toll-like receptor 4 antibody can alleviate APAP-induced acute liver injury through the change of the gut microbiota, metabolic pathways, and gut barrier function. This work suggested the gut… read more here.
Keywords: microbiota; gut microbiota; liver injury; acute liver ... See more keywords