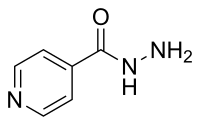
Honokiol alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via decreasing generation of acetaminophen-protein adducts in liver.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Life sciences"
DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.062
Abstract: AIM Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is the most frequent cause of drug-induced liver damage. Magnolia officinalis is a traditional hepatoprotective Chinese medicine and Honokiol (HO) is the major active constituent. The present study was to investigate… read more here.
Keywords: protein adducts; induced hepatotoxicity; generation; apap ... See more keywords

Role of extracellular vesicles in release of protein adducts after acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice and humans.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Toxicology letters"
DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.11.005
Abstract: Formation of acetaminophen (APAP) protein adducts are a critical feature of APAP hepatotoxicity, and circulating protein adducts have recently been utilized in bioassays for identification of APAP overdose in humans. Despite their clinical significance, mechanisms… read more here.
Keywords: protein adducts; apap overdose; release; apap protein ... See more keywords