
An adult case of NOTCH3 mutation in pulmonary artery hypertension
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Pulmonary Circulation"
DOI: 10.1002/pul2.12050
Abstract: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a progressively fatal disease process affecting the small distal arteries of the pulmonary vasculature. It is characterized by vascular remodeling, proliferation, and subsequent vasocontraction leading to right heart failure. In… read more here.
Keywords: case notch3; hypertension; notch3 mutation; pulmonary artery ... See more keywords

Outcomes of infants and children undergoing surgical repair of ventricular septal defect: a review of the literature and implications for research with an emphasis on pulmonary artery hypertension
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Cardiology in the Young"
DOI: 10.1017/s1047951120001146
Abstract: Abstract Background: Pulmonary vascular disease resulting from CHDs may be the most preventable cause of pulmonary artery hypertension worldwide. Many children in developing countries still do not have access to early closure of clinically significant… read more here.
Keywords: pulmonary artery; artery hypertension; ventricular septal; septal defect ... See more keywords

Protective effects of Dapagliflozin on the vulnerability of ventricular arrhythmia in rats with pulmonary artery hypertension induced by monocrotaline
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Bioengineered"
DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2017652
Abstract: ABSTRACT Monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) has been reported to cause right heart failure (RHF). Moreover, Right heart diseases have been determined to cause ventricular arrhythmia (VA). So we can conclude that MCT-induced PAH… read more here.
Keywords: mct; pulmonary artery; ventricular arrhythmia; pah ... See more keywords

MicroRNA-98 can serve as a diagnostic marker for congenital heart disease-associated pulmonary artery hypertension
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Chinese Medical Journal"
DOI: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000001193
Abstract: Congenital heart disease (CHD) has become the leading the instructions of a qPCR kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, mortal cause for an infant from congenital abnormalities. Shanghai, China). The relative expression of miR-98 was Pulmonary artery… read more here.
Keywords: heart disease; pulmonary artery; congenital heart; artery hypertension ... See more keywords
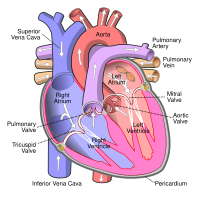
Increased Mitochondrial Calcium Fluxes in Hypertrophic Right Ventricular Cardiomyocytes from a Rat Model of Pulmonary Artery Hypertension
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Life"
DOI: 10.3390/life13020540
Abstract: Simple Summary In pulmonary artery hypertension, right ventricular (RV) afterload is increased, which requires the cardiomyocytes to contract with greater force against the additional pulmonary artery pressure. In response, RV cardiomyocytes increase contractile protein content… read more here.
Keywords: pulmonary artery; artery hypertension; right ventricular; ca2 ... See more keywords