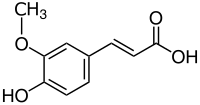
Bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds in common beans ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) after in vitro gastrointestinal digestion: A comparison of two cooking procedures
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Cereal Chemistry"
DOI: 10.1002/cche.10283
Abstract: Background and objectives: Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) are widely consumed, but the bioaccessibility of their phenolic compounds (PCs) may be affected by different factors. Within this framework, an in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of two bean… read more here.
Keywords: bioaccessibility phenolic; bioaccessibility; phaseolus vulgaris; beans phaseolus ... See more keywords

Effect of cooking on aroma profile of red kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) and correlation with sensory quality.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Food chemistry"
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.149
Abstract: Volatile aroma compounds of three varieties of red kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) namely Kashmiri red, Sharmili and Chitra were extracted in raw state using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and cooked state using simultaneous distillation extraction (SDE).… read more here.
Keywords: red kidney; aroma; kidney beans; phaseolus vulgaris ... See more keywords

The effects of blanching on composition and modification of proteins in navy beans (Phaseolus vulgaris).
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Food chemistry"
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128950
Abstract: Blanching is an important process in the preparation of navy beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) for canning. We here explore the effect of blanching which can profoundly affect protein composition and introduce protein-primary-level modifications. Amino acid… read more here.
Keywords: protein; navy beans; beans phaseolus; phaseolus vulgaris ... See more keywords

Thermal treatment of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): Factors determining cooking time and its consequences for sensory and nutritional quality.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety"
DOI: 10.1111/1541-4337.12770
Abstract: Over the past years, the shift toward plant-based foods has largely increased the global awareness of the nutritional importance of legumes (common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in particular) and their potential role in sustainable food… read more here.
Keywords: nutritional quality; time; phaseolus vulgaris; beans phaseolus ... See more keywords

Non-polar metabolites of green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) potentiate the antidiabetic activity of mesenchymal stem cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of food biochemistry"
DOI: 10.1111/jfbc.14083
Abstract: Green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) are consumed as pods or mature seeds (common beans). The pods were extracted with 95% ethanol and processed to prepare non-polar and polar fractions. Comparing the antihyperglycemic activity of both… read more here.
Keywords: green beans; beans phaseolus; non polar; activity ... See more keywords