
Sero‐detection of Coxiella burnetii infection in cattle, sheep and goats in selected regions of Nepal
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Veterinary Medicine and Science"
DOI: 10.1002/vms3.458
Abstract: Abstract Coxiella burnetii, a Gram‐negative bacterium is a zoonotic agent causing coxiellosis in animals. Small ruminants and cattle are the primary reservoirs for human infection. This study was aimed to estimate the sero‐prevalence of C.… read more here.
Keywords: cattle sheep; infection; regions nepal; coxiella burnetii ... See more keywords

Detection of Coxiella burnetii DNA and anti-Coxiella burnetii IgG antibodies in precolostral blood samples of stillborn calves in an endemically infected Holstein dairy herd
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Folia Microbiologica"
DOI: 10.1007/s12223-017-0553-4
Abstract: Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii), an intracellular zoonotic bacterium causing Q fever, occurs widely in cattle herds. After invasion of the pregnant uterus and initial localization in the placenta, active C. burnetii infections may spread to… read more here.
Keywords: precolostral blood; blood samples; coxiella burnetii; stillborn calves ... See more keywords

The burden of Coxiella burnetii among aborted dairy animals in Egypt and its public health implications.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Acta tropica"
DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.11.011
Abstract: Q fever is a zoonotic disease of mounting public health implications. Dairy animals are major reservoir for such disease whereas abortion is the main clinical outcome. The current study was conducted to investigate the burden… read more here.
Keywords: dairy animals; animals egypt; burnetii; public health ... See more keywords
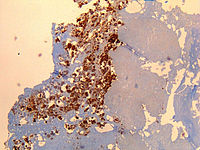
Coxiella burnetii in dairy goats with a history of reproductive disorders in Brazil.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Acta tropica"
DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.04.010
Abstract: Coxiella burnetii, an intracellular bacterium, is the agent of Q fever/coxiellosis, a worldwide zoonosis. Dairy animals are the primary reservoirs of C. burnetii, and although the disease is usually asymptomatic or subclinical, abortion is a… read more here.
Keywords: dairy goats; history reproductive; coxiella burnetii; burnetii ... See more keywords

Coxiella burnetii in camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Algeria: seroprevalence, molecular characterization, and ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) vectors.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Acta tropica"
DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105443
Abstract: Q fever is a widespread zoonotic disease caused by Coxiella burnetii that most commonly infects not only a variety of mammals but also arthropods and in particularly ticks. The aim of this study was to detect… read more here.
Keywords: seroprevalence; coxiella burnetii; burnetii camels; burnetii ... See more keywords

Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii in milk collected from buffalo (water buffalo) and cattle dairy farms in Northwest of Iran.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Comparative immunology, microbiology and infectious diseases"
DOI: 10.1016/j.cimid.2019.101368
Abstract: The present study was conducted to determine the prevalence of C. burnetii in raw milk samples collected from water buffalos and cattle in Northwest of Iran (West Azerbaijan Province). A total number of 840 milk… read more here.
Keywords: milk; buffalo cattle; prevalence; burnetii ... See more keywords

Streptococcus anginosus and Coxiella burnetii vascular graft co-infection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "IDCases"
DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00697
Abstract: Vascular graft infections are rare complications, usually associated with a monomicrobial pyogenic culture. We report a case of vascular graft co-infection with Streptococcus anginosus and Coxiella burnetii, complicated by an aorto-duodenal fistula. Screening for chronic… read more here.
Keywords: vascular graft; graft; streptococcus anginosus; burnetii ... See more keywords

Molecular survey on the occurrence of avian haemosporidia, Coxiella burnetii and Francisellatularensis in waterfowl from central Italy
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2019.07.008
Abstract: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the occurrence of some avian Haemosporidia, Coxiella burnetii and Francisella tularensis in waterfowl from Tuscany wetlands. One-hundred and thirty-three samples of spleen were collected from regularly… read more here.
Keywords: waterfowl; haemosporidia coxiella; coxiella burnetii; burnetii ... See more keywords

Molecular detection and genetic characterization of the potentially pathogenic Coxiella burnetii and the endosymbiotic Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii in ticks infesting camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Tunisia.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Microbial pathogenesis"
DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103655
Abstract: Tick-borne bacteria are considered to be emerging in camels, but data about their occurrence in Tunisian dromedaries and their infesting ticks remain scarce. In this study, 412 camel blood samples and 327 partially engorged ticks… read more here.
Keywords: coxiella burnetii; midichloria mitochondrii; candidatus midichloria; burnetii ... See more keywords

Coxiella burnetii seroprevalence and Q fever in Australian wildlife rehabilitators
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "One Health"
DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2020.100197
Abstract: Coxiella burnetii is the causative bacterium of the zoonotic disease Q fever, which is recognised as a public health concern globally. Macropods have been suggested as a potential source of C. burnetii infection for humans.… read more here.
Keywords: fever; australian wildlife; coxiella burnetii; burnetii ... See more keywords

Investigation of Ixodidae ticks infesting camels at slaughterhouse and its potential role in transmitting Coxiella burnetii in Egypt
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Small Ruminant Research"
DOI: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2020.106173
Abstract: Abstract Coxiella burnetii is an important pathogen because of its wide host range, low infectious dose, stability in the environment, and capability for aerosol dispersion. The aim of this work was to investigate the potential… read more here.
Keywords: coxiella burnetii; potential role; burnetii; transmitting coxiella ... See more keywords