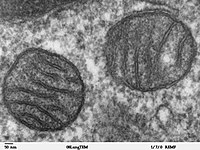
Selective induction of cancer cell death by VDAC1‐based peptides and their potential use in cancer therapy
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Molecular Oncology"
DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12313
Abstract: Mitochondrial VDAC1 mediates cross talk between the mitochondria and other parts of the cell by transporting anions, cations, ATP, Ca2+, and metabolites and serves as a key player in apoptosis. As such, VDAC1 is involved… read more here.
Keywords: cell death; vdac1 based; cancer cell; cancer ... See more keywords

SIK2 promotes ovarian cancer cell motility and metastasis by phosphorylating MYLK
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Molecular Oncology"
DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13208
Abstract: Salt‐inducible kinase 2 (SIK2; also known as serine/threonine‐protein kinase SIK2) is overexpressed in several cancers and has been implicated in cancer progression. However, the mechanisms by which SIK2 regulates cancer cell motility, migration and metastasis… read more here.
Keywords: ovarian cancer; cancer; cancer cell; cell motility ... See more keywords

TGFβ selects for pro-stemness over pro-invasive phenotypes during cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Molecular oncology"
DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13215
Abstract: Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which correlates with stemness and invasiveness. Mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) is induced by TGFβ withdrawal and correlates with metastatic colonization. Whether TGFβ promotes stemness and invasiveness simultaneously… read more here.
Keywords: mesenchymal transition; cancer cell; tgf; pro stemness ... See more keywords

CDK6 is activated by the atypical cyclin I to promote E2F-mediated gene expression and cancer cell proliferation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Molecular oncology"
DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13438
Abstract: Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), together with their cyclin partners, are the master cell cycle regulators. Remarkably, the cyclin family was extended to include atypical cyclins, characterized by distinctive structural features, but their partner CDKs remain elusive.… read more here.
Keywords: cell; cdk6; cancer cell; cyclin ... See more keywords

The Use of Microfluidic Platforms to Probe the Mechanism of Cancer Cell Extravasation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Advanced healthcare materials"
DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201901410
Abstract: Powerful experimental tools have contributed a wealth of novel insight into cancer etiology from the organ to the subcellular levels. However, these advances in understanding have outpaced improvements in clinical outcomes. One possible reason for… read more here.
Keywords: microfluidic platforms; use microfluidic; cell extravasation; cancer cell ... See more keywords

NNMT‐DNMT1 Axis is Essential for Maintaining Cancer Cell Sensitivity to Oxidative Phosphorylation Inhibition
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Advanced Science"
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202202642
Abstract: Lacking a clear understanding of the molecular mechanism determining cancer cell sensitivity to oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) inhibition limits the development of OXPHOS‐targeting cancer treatment. Here, cancer cell lines sensitive or resistant to OXPHOS inhibition are… read more here.
Keywords: inhibition; sensitivity; oxphos inhibition; cancer cell ... See more keywords

Facile synthesis of C6‐substituted benz[4,5]imidazo[1,2‐a]quinoxaline derivatives and their anticancer evaluation
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Archiv der Pharmazie"
DOI: 10.1002/ardp.202000393
Abstract: Cancer remains a leading cause of death worldwide, resulting in continuous efforts to discover and develop highly efficacious anticancer drugs. High‐throughput screening of heterocyclic compound libraries is one of the promising approaches that provided several… read more here.
Keywords: quinoxaline derivatives; cell; cell line; cancer cell ... See more keywords
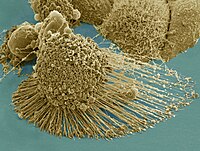
Upregulation of BAX and caspase‐3, as well as downregulation of Bcl‐2 during treatment with indeno[1,2‐b]quinoxalin derivatives, mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Archiv der Pharmazie"
DOI: 10.1002/ardp.202100454
Abstract: Cancer is the world's foremost cause of death. There are over 100 different forms of cancer. Cancers are frequently named after the organs or tissues in which they develop. As a part of our aim… read more here.
Keywords: cell; cell line; human cancer; downregulation bcl ... See more keywords

lncRNA‐NKILA/NF‐κB feedback loop modulates laryngeal cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and radioresistance
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Cancer Medicine"
DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1405
Abstract: Laryngeal cancer is one of the most common head and neck malignant tumors and is commonly resistant to X‐ray‐based radiotherapy. NF‐κB interacting lncRNA (NKILA) has been reported to serve as a tumor suppressor in several… read more here.
Keywords: lncrna nkila; laryngeal cancer; feedback loop; cancer cell ... See more keywords

TNPO2 operates downstream of DYNC1I1 and promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Cancer Medicine"
DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2582
Abstract: The import of proteins into the nucleus plays an important role in tumor development. In addition to the classical nuclear import proteins importin‐β and importin‐α, there are many nonclassical nuclear import proteins that include TNPO2.… read more here.
Keywords: gastric cancer; downstream dync1i1; proliferation; tnpo2 ... See more keywords

Upregulation of long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation and migration
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Cancer Medicine"
DOI: 10.1002/cam4.994
Abstract: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), a novel class of transcripts that have critical roles in carcinogenesis and progression, have emerged as important gene expression modulators. Recent evidence indicates that lncRNA taurine‐upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) functions as… read more here.
Keywords: tug1; long noncoding; cervical cancer; cancer cell ... See more keywords