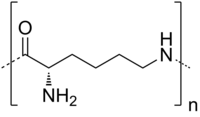
Fabrication and characterization of antibacterial epsilon-poly-L-lysine anchored dicarboxyl cellulose beads.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Carbohydrate polymers"
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117337
Abstract: Pathogens in the food and environment pose a great threat to human health. To solve this problem, we described a novel route to synthesize antibacterial epsilon-poly-L-lysine (EPL) anchored dicarboxyl cellulose beads. Cellulose beads were prepared… read more here.
Keywords: poly lysine; epsilon poly; antibacterial epsilon; anchored dicarboxyl ... See more keywords

Magnetically driven release of dopamine from magnetic-non-magnetic cellulose beads
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of Molecular Liquids"
DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114290
Abstract: Abstract Passive devices that exhibit release of the drug on demand and have the potential to be switched off and on optimally and effectively are advantageous for the treatment of various diseases including diabetes, chronic… read more here.
Keywords: drug; magnetic non; cellulose beads; release ... See more keywords

Removal of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii) from wastewater using arginine cross-linked chitosan–carboxymethyl cellulose beads as green adsorbent
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "RSC Advances"
DOI: 10.1039/c9ra00356h
Abstract: Remediation of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii) containing wastewater by arginine crosslinked chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose beads. read more here.
Keywords: wastewater using; removal wastewater; carboxymethyl cellulose; chitosan carboxymethyl ... See more keywords

Semipermeable Cellulose Beads Allow Selective and Continuous Release of Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEV) From Encapsulated Cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Frontiers in Pharmacology"
DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00679
Abstract: The clinical benefit of therapies using Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) is attributable to their pleiotropic effect over cells and tissues, mainly through their secretome. This paracrine effect is mediated by secreted growth factors and extracellular… read more here.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; release small; sev; cellulose beads ... See more keywords