
Seed rain and soil seed bank in Chinese fir plantations and an adjacent natural forest in southern China: Implications for the regeneration of native species
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Ecology and Evolution"
DOI: 10.1002/ece3.8539
Abstract: Abstract The natural regeneration of native broadleaved species underneath forest monoculture plantations is important to recover ecosystem functions and to mitigate adverse environmental effects. To understand how seed rain and soil seed bank facilitate natural… read more here.
Keywords: seed rain; soil seed; seed bank; seed ... See more keywords

A real-time PCR for detection of pathogens of anthracnose on Chinese fir using TaqMan probe targeting ApMat gene.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Pest management science"
DOI: 10.1002/ps.7260
Abstract: BACKGROUND Anthracnose is one of the most widespread and destructive diseases on Chinese fir. Colletotrichum cangyuanense, C. fructicola, C. gloeosporioides, and C. siamense are the causal agents of anthracnose on Chinese fir. A rapid and… read more here.
Keywords: gloeosporioides siamense; time pcr; fructicola gloeosporioides; real time ... See more keywords

Investigation of drying characteristics in superheated steam drying of UF-impregnated Chinese fir
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "European Journal of Wood and Wood Products"
DOI: 10.1007/s00107-017-1245-0
Abstract: Urea formaldehyde (UF) resin-impregnated Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.)Hook.) was dried at different temperatures in an atmospheric pressure superheated steam dryer. Drying characteristics, moisture content, drying rate, temperature profile, drying defects, and color change were… read more here.
Keywords: impregnated chinese; drying characteristics; chinese fir; superheated steam ... See more keywords

Broadleaf trees mediate chemically the growth of Chinese fir through root exudates
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Biology and Fertility of Soils"
DOI: 10.1007/s00374-019-01389-0
Abstract: Tree performance in mixed-species forest plantations is ultimately the net result of positive and negative interactions among species. Despite increasing knowledge of interspecific interactions, relatively little is known about the chemical mechanisms mediating such interactions.… read more here.
Keywords: growth; root exudates; growth chinese; chinese fir ... See more keywords
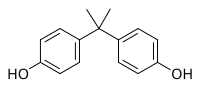
Allelochemical-driven N preference switch from NO3− to NH4+ affecting plant growth of Cunninghamia lanceolata (lamb.) hook
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Plant and Soil"
DOI: 10.1007/s11104-020-04539-8
Abstract: Nitrogen (N) application is often known to influence various properties in Chinese fir growth, but the regeneration failure and productivity decline in Chinese fir plantations are often affected by allelochemical compounds. Little is known about… read more here.
Keywords: plant growth; chinese fir; growth; no3 nh4 ... See more keywords
Does root respiration of subtropical Chinese fir seedlings acclimate to seasonal temperature variation or experimental soil warming
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Agricultural and Forest Meteorology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108612
Abstract: Abstract Although subtropical forests play a key role in global carbon budget, how the root respiration, a substantial part of ecosystem carbon flux, responds to ongoing climate warming in this ecosystem is not well understood.… read more here.
Keywords: temperature variation; respiration; root respiration; chinese fir ... See more keywords

Evaluating the mechanical and fire-resistance properties of modified fast-growing Chinese fir timber with boric-phenol-formaldehyde resin
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Construction and Building Materials"
DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.035
Abstract: Abstract The abundant fast-growing Chinese fir was confined to nonstructural use for its poor mechanical and fire performance, and classified as low-quality building materials. Herein, Chinese fir was impregnated with boric-phenol-formaldehyde (BPF) resin, and then… read more here.
Keywords: boric phenol; fast growing; phenol formaldehyde; mechanical fire ... See more keywords

Use impregnation and densification to improve mechanical properties and combustion performance of Chinese fir
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Construction and Building Materials"
DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118101
Abstract: Abstract The abundant fast-growing Chinese fir is a low-grade building material due to its low mechanical strength and poor combustion performance. The impregnation with boric phenol formaldehyde resin (BPF) improve the mechanical properties and combustion… read more here.
Keywords: properties combustion; combustion performance; impregnation; mechanical properties ... See more keywords

Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on Chinese fir sapling growth in Southern China.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Ecotoxicology and environmental safety"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.071
Abstract: The influence of acid rain on plant growth includes direct effects on foliage as well as indirect soil-mediated effects that cause a reduction in root growth. In addition, the concentration of NO3- in acid rain… read more here.
Keywords: acid rain; fir sapling; chinese fir; growth ... See more keywords

Responses of Chinese fir and Schima superba seedlings to light gradients: Implications for the restoration of mixed broadleaf-conifer forests from Chinese fir monocultures
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Forest Ecology and Management"
DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2018.03.033
Abstract: Abstract Although Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook) plantations are widely grown for timber production in southern China, they have low biodiversity and provide limited ecosystem services. To address this problem, C. lanceolata are increasingly… read more here.
Keywords: mixed broadleaf; light gradients; superba seedlings; chinese fir ... See more keywords

Leaf litter carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) across China
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Global Ecology and Conservation"
DOI: 10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01542
Abstract: Abstract The stochiometric characteristics of plant tissue (living or dead) can influence carbon (C) and nutrient dynamics in forest ecosystems. Numerous investigations have focused on green leaves in site or regional areas, but few on… read more here.
Keywords: litter; leaf litter; stoichiometry; chinese fir ... See more keywords