
Anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant phenylpropanoids from Chinese olive.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Food chemistry"
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.031
Abstract: Chinese olive is served as a famous fruit and traditional herb in China. In this study, the anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant phytochemicals of Chinese olive fruits were investigated. Three new phenylpropanoids (2, 6, 19), together with… read more here.
Keywords: neuroinflammatory antioxidant; antioxidant phenylpropanoids; phenylpropanoids chinese; anti neuroinflammatory ... See more keywords

Identification of Scoparone from Chinese Olive Fruit as a Modulator of Macrophage Polarization.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Journal of agricultural and food chemistry"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c08132
Abstract: Chinese olive (Canarium album L.) has been highlighted for its remarkable health benefits. We previously showed that the ethyl acetate fraction of Chinese olive (COE) is an effective anti-inflammatory agent. In this study, we used… read more here.
Keywords: scoparone; chinese olive; fruit; anti inflammatory ... See more keywords

Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Capacity of Chinese Olive (Canarium album L.) Cultivars.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of food science"
DOI: 10.1111/1750-3841.13740
Abstract: In this study, the physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant potentials of 10 Chinese olive cultivars were investigated. Considerable differences were found between cultivars in weight, edible yield, water content, size, shape, total soluble solids, and total… read more here.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; capacity chinese; physicochemical properties; chinese olive ... See more keywords
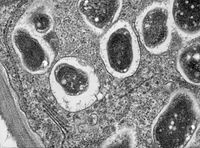
Antifungal Activity and Action Mechanism of Ginger Oleoresin Against Pestalotiopsis microspora Isolated From Chinese Olive Fruits
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Frontiers in Microbiology"
DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02583
Abstract: Pestalotiopsis microspora (P. microspora) is one of dominant pathogenic fungi causing rotten disease in harvested Chinese olive (Canarium album Lour.) fruits. The purposes of this study were to evaluate the antifungal activities of ginger oleoresin… read more here.
Keywords: antifungal activity; concentration; pestalotiopsis microspora; chinese olive ... See more keywords