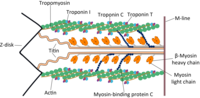
Point mutations in the tri-helix bundle of the M-domain of cardiac myosin binding protein-C influence systolic duration and delay cardiac relaxation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.05.001
Abstract: Cardiac myosin binding protein-C (cMyBP-C) is an essential regulatory protein required for proper systolic contraction and diastolic relaxation. We previously showed that N'-terminal domains of cMyBP-C stimulate contraction by binding to actin and activating the… read more here.
Keywords: myosin binding; relaxation; binding protein; binding actin ... See more keywords

Variable cardiac myosin binding protein-C expression in the myofilaments due to MYBPC3 mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.08.023
Abstract: BACKGROUND Mutations in MYBPC3 are the most common cause of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). These mutations produce dysfunctional protein that is quickly degraded and not incorporated in the myofilaments. Most patients are heterozygous and allelic expression… read more here.
Keywords: protein; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; expression; cell ... See more keywords

Modulation of myosin by cardiac myosin binding protein-C peptides improves cardiac contractility in ex-vivo experimental heart failure models
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08169-1
Abstract: Cardiac myosin binding protein-C (cMyBP-C) is an important regulator of sarcomeric function. Reduced phosphorylation of cMyBP-C has been linked to compromised contractility in heart failure patients. Here, we used previously published cMyBP-C peptides 302A and… read more here.
Keywords: contractility; cmybp; heart failure; myosin ... See more keywords

Site-specific phosphorylation of myosin binding protein-C coordinates thin and thick filament activation in cardiac muscle
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America"
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1903033116
Abstract: Significance Phosphorylation of cardiac myosin binding protein-C (cMyBP-C) is a key regulator of myocardial contractility, and dephosphorylation of cMyBP-C is associated with heart failure. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying contractile regulation by cMyBP-C phosphorylation are… read more here.
Keywords: phosphorylation; myosin binding; binding protein; cmybp ... See more keywords

Making Sense of Inhibiting Nonsense in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Circulation"
DOI: 10.1161/circulationaha.118.037936
Abstract: The adult heart is 1 of the tissues least capable of regeneration and repair, with estimates of ≈0.5% to 2% nuclear DNA synthesis events per year in cardiomyocytes.1 Hence, it requires efficient surveillance systems to… read more here.
Keywords: mrna; cmybp; quality control; mechanism ... See more keywords