
First report of Coxiella burnetii and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in poultry red mites, Dermanyssus gallinae (Mesostigmata, Acari), related to urban outbreaks of dermatitis in Italy
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "New Microbes and New Infections"
DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2018.01.004
Abstract: The poultry red mite (PRM), Dermanyssus gallinae, is a nonburrowing haematophagous nest-dwelling ectoparasite of birds; occasionally it bites humans, inducing dermatitis. The possibility that this parasite may also be involved in transmission of pathogens is… read more here.
Keywords: sensu lato; burgdorferi sensu; coxiella;

Molecular investigation into the presence of a Coxiella sp. in Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks in Australia.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Veterinary microbiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.01.021
Abstract: Q fever is an infectious disease with a global distribution caused by the intracellular bacterium, Coxiella burnetii, which has been detected in a large number of tick species worldwide, including the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus… read more here.
Keywords: presence; investigation; rhipicephalus sanguineus; coxiella ... See more keywords
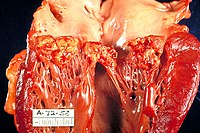
Contemporary diagnostics for medically relevant fastidious microorganisms belonging to the genera Anaplasma,Bartonella,Coxiella,OrientiaandRickettsia
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "FEMS Microbiology Reviews"
DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuac013
Abstract: Abstract Many of the human infectious pathogens—especially the zoonotic or vector-borne bacteria—are fastidious organisms that are difficult to cultivate because of their strong adaption to the infected host culminating in their near-complete physiological dependence on… read more here.
Keywords: coxiella; spp; contemporary diagnostics; bartonella ... See more keywords

Evolutionary changes in symbiont community structure in ticks
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Molecular Ecology"
DOI: 10.1111/mec.14094
Abstract: Ecological specialization to restricted diet niches is driven by obligate, and often maternally inherited, symbionts in many arthropod lineages. These heritable symbionts typically form evolutionarily stable associations with arthropods that can last for millions of… read more here.
Keywords: maternally inherited; community structure; tick species; structure ... See more keywords

Perturbation of ATG16L1 function impairs the biogenesis of Salmonella and Coxiella replication vacuoles
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Molecular Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14858
Abstract: Anti‐bacterial autophagy, known as xenophagy, is a host innate immune response that targets invading pathogens for degradation. Some intracellular bacteria, such as the enteric pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium), utilize effector proteins to… read more here.
Keywords: typhimurium; coxiella; perturbation atg16l1; biogenesis ... See more keywords

An outbreak of crayfish rickettsiosis caused by Coxiella cheraxi in redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) imported to Israel from Australia.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Transboundary and emerging diseases"
DOI: 10.1111/tbed.14375
Abstract: The redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) is a freshwater decapod crustacean, cultured in numerous countries worldwide for both food and ornamental purposes. Redclaw crayfish has become an important aquaculture species due to its physical and biological… read more here.
Keywords: coxiella; redclaw crayfish; cherax quadricarinatus; coxiella cheraxi ... See more keywords

Coxiella burnetii Plasmid Effector B Promotes LC3-II Accumulation and Contributes To Bacterial Virulence in a SCID Mouse Model
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Infection and Immunity"
DOI: 10.1128/iai.00016-22
Abstract: Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of zoonotic Q fever, is characterized by replicating inside the lysosome-derived Coxiella-containing vacuole (CCV) in host cells. Some effector proteins secreted by C. burnetii have been reported to be involved… read more here.
Keywords: lc3 accumulation; plasmid; coxiella; coxiella burnetii ... See more keywords
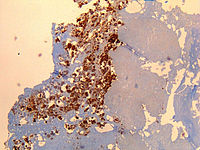
Coxiella burnetii Epitope-Specific T-Cell Responses in Patients with Chronic Q Fever
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Infection and Immunity"
DOI: 10.1128/iai.00213-19
Abstract: Infection with Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever, can result in life-threatening persistent infection. Reactogenicity hinders worldwide implementation of the only licensed human Q fever vaccine. We previously demonstrated long-lived immunoreactivity in individuals… read more here.
Keywords: chronic fever; coxiella; fever; infection ... See more keywords

TGF-β/IFN-γ Antagonism in Subversion and Self-Defense of Phase II Coxiella burnetii-Infected Dendritic Cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Infection and Immunity"
DOI: 10.1128/iai.00323-22
Abstract: Dendritic cells (DCs) belong to the first line of innate defense and come into early contact with invading pathogens, including the zoonotic bacterium Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever. However, the pathogen-host cell… read more here.
Keywords: coxiella; defense; subversion; self defense ... See more keywords

A Farnesylated Coxiella burnetii Effector Forms a Multimeric Complex at the Mitochondrial Outer Membrane during Infection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Infection and Immunity"
DOI: 10.1128/iai.01046-16
Abstract: ABSTRACT Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever, establishes a unique lysosome-derived intracellular niche termed the Coxiella-containing vacuole (CCV). The Dot/Icm-type IVB secretion system is essential for the biogenesis of the CCV and the… read more here.
Keywords: coxiella; effector; outer membrane; mitochondrial outer ... See more keywords

Coxiella burnetii RpoS Regulates Genes Involved in Morphological Differentiation and Intracellular Growth
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of Bacteriology"
DOI: 10.1128/jb.00009-19
Abstract: The Q fever bacterium Coxiella burnetii has spore-like environmental stability, a characteristic that contributes to its designation as a potential bioweapon. Stability is likely conferred by a highly resistant, small cell variant (SCV) stationary-phase form… read more here.
Keywords: genes involved; growth; coxiella; cell ... See more keywords