
Maximal Force Increases at Physiological Temperature in Myocardial Strips from Non-Failing and Failing Human Hearts
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Biophysical Journal"
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.675
Abstract: Heart failure contributes to 1 in 9 deaths in the United States. Contractile deficits at the myofilament level may contribute to the heart inadequately pumping blood throughout the body. Yet, few studies have investigated force… read more here.
Keywords: temperature; failing failing; non failing; force ... See more keywords

Omecamtiv Mecarbil Slows Myosin Kinetics in Skinned Rat Myocardium at Physiological Temperature.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Biophysical journal"
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.04.020
Abstract: Heart failure is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the heart muscle becomes weakened and cannot adequately circulate blood and nutrients around the body. Omecamtiv mecarbil (OM) is a compound that has been developed to… read more here.
Keywords: cross bridge; bridge; physiological temperature; activation ... See more keywords

Cross-bridge mechanics estimated from skeletal muscles’ work-loop responses to impacts in legged locomotion
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-02819-6
Abstract: Legged locomotion has evolved as the most common form of terrestrial locomotion. When the leg makes contact with a solid surface, muscles absorb some of the shock-wave accelerations (impacts) that propagate through the body. We… read more here.
Keywords: cross bridge; usepackage; mechanics; document ... See more keywords

Muscle thixotropy-where are we now?
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of applied physiology"
DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00788.2018
Abstract: Relaxed skeletal muscle has an inbuilt resistance to movement. In particular, the resistance manifests itself as a substantial stiffness for small movements. The stiffness is impermanent, because it forms only when the muscle is stationary… read more here.
Keywords: movement; muscle; muscle thixotropy; resistance ... See more keywords
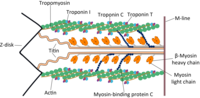
Slower Calcium Handling Balances Faster Cross-Bridge Cycling in Human MYBPC3 HCM
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Circulation Research"
DOI: 10.1161/circresaha.122.321956
Abstract: Background: The pathogenesis of MYBPC3-associated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is still unresolved. In our HCM patient cohort, a large and well-characterized population carrying the MYBPC3:c772G>A variant (p.Glu258Lys, E258K) provides the unique opportunity to study the basic… read more here.
Keywords: hcm; mybpc3; cross bridge; bridge cycling ... See more keywords

Sensitivity of muscle force response of a two-state cross-bridge model to variations in model parameters
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine"
DOI: 10.1177/09544119221122062
Abstract: Muscle models based on the cross-bridge theory (Huxley-type models) are frequently used to calculate muscle forces for different contractile conditions. Dynamic and nonlinear characteristics of muscle forces produced during isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions can… read more here.
Keywords: model parameters; muscle; bridge; force ... See more keywords

Effects of cross-bridge compliance on the force-velocity relationship and muscle power output
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "PLoS ONE"
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190335
Abstract: Muscles produce force and power by utilizing chemical energy through ATP hydrolysis. During concentric contractions (shortening), muscles generate less force compared to isometric contractions, but consume greater amounts of energy as shortening velocity increases. Conversely,… read more here.
Keywords: bridge; velocity; compliance; force ... See more keywords

A mechanistic model of cross-bridge migration in RBC aggregation and disaggregation
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology"
DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1049878
Abstract: Red blood cells (RBCs) clump together under low flow conditions in a process called RBC aggregation, which can alter RBC perfusion in a microvascular network. As elevated RBC aggregation is commonly associated with cardiovascular and… read more here.
Keywords: rbc; rbc aggregation; disaggregation; cross ... See more keywords

Non-cross Bridge Viscoelastic Elements Contribute to Muscle Force and Work During Stretch-Shortening Cycles: Evidence From Whole Muscles and Permeabilized Fibers
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Frontiers in Physiology"
DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.648019
Abstract: The sliding filament–swinging cross bridge theory of skeletal muscle contraction provides a reasonable description of muscle properties during isometric contractions at or near maximum isometric force. However, it fails to predict muscle force during dynamic… read more here.
Keywords: force work; cross bridge; force;

Linear and Nonlinear Photon-Induced Cross Bridge/Space Charge Transfer in STC Molecular Crystals
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Nanomaterials"
DOI: 10.3390/nano12030535
Abstract: In this work, we theoretically studied the optical absorption properties of a layer-stacked cocrystal heterogeneous material Spe-TCNB cocrystal (STC) which is produced by supramolecular self-assembly of organic conjugated monomers SPE and TCNB. The highly ordered… read more here.
Keywords: cross bridge; charge transfer; space charge; charge ... See more keywords