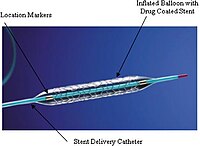
Drug‐coated balloons for the treatment of in‐stent restenosis in diabetic patients: A review of currently available scientific data
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions"
DOI: 10.1002/ccd.26957
Abstract: After the introduction of drug eluting stent (DES) the rate of in‐stent restenosis (ISR) has decreased if compared to the BMS era; however, treatment of patients with ISR remained a major issue for the interventional… read more here.
Keywords: treatment; stent restenosis; drug; diabetic patients ... See more keywords

Impact of dual antiplatelet therapy duration on 1‐year clinical outcomes in diabetic patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: Insights from the real‐world OPT‐CAD study
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions"
DOI: 10.1002/ccd.28653
Abstract: To investigate the optimal dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) duration for diabetic patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). read more here.
Keywords: patients acute; dual antiplatelet; antiplatelet therapy; diabetic patients ... See more keywords

Long‐term follow‐up of contemporary drug‐eluting stent implantation in diabetic patients: Subanalysis of a randomized controlled trial
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions"
DOI: 10.1002/ccd.30545
Abstract: The elevated risk of adverse events following percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic patients persists with newer‐generation DES. The polymer‐free amphilimus‐eluting stent (PF‐AES) possesses characteristics with a potentially enhanced performance in patients with diabetes. Data from… read more here.
Keywords: long term; drug eluting; eluting stent; contemporary drug ... See more keywords

The changes in levels of blood cortisol, glucose, and oxygen saturation in type 2 diabetic patients during tooth extraction
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Clinical and Experimental Dental Research"
DOI: 10.1002/cre2.641
Abstract: The extraction of a tooth exacerbates the stress in diabetic patients leading to diabetic complications so the aim was to evaluate the changes in blood cortisol, glucose, and oxygen saturation in type 2 diabetic patients… read more here.
Keywords: glucose oxygen; oxygen saturation; saturation type; blood cortisol ... See more keywords

Anti-inflammatory effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in COVID-19.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "IUBMB life"
DOI: 10.1002/iub.2719
Abstract: The ongoing pandemic of COVID-19 is intrinsically a systemic inflammatory disorder; hence, those patients suffering an underlying chronic inflammatory disease such as diabetes mellitus are at high risk of severe complications. Preventing or suppressing the… read more here.
Keywords: sodium glucose; glucose cotransporter; anti inflammatory; diabetic patients ... See more keywords

Improved angiogenic activity of endothelial progenitor cell in diabetic patients treated with insulin plus metformin
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of Cellular Biochemistry"
DOI: 10.1002/jcb.27985
Abstract: Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is associated with an increased vascular disease. Moreover, endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) function is impaired in diabetic patients. Decreased EPC number plays a critical role in reduced endothelial repair and development… read more here.
Keywords: insulin plus; patients treated; plus metformin; diabetic patients ... See more keywords
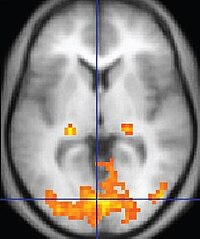
A promising structural magnetic resonance imaging assessment in patients with preclinical cognitive decline and diabetes mellitus
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of Cellular Physiology"
DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28359
Abstract: Subjective cognitive decline (SCD) is frequently reported in diabetic patients. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with changes in the microstructure of the brain arise in diabetic patients, including changes in gray matter volume (GMV). However,… read more here.
Keywords: structural magnetic; magnetic resonance; diabetic patients; cognitive impairment ... See more keywords

Coronary atherosclerotic burden vs. coronary vascular function in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with normal myocardial perfusion: a propensity score analysis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging"
DOI: 10.1007/s00259-017-3671-y
Abstract: PurposeTo assess the relationship between coronary atherosclerotic burden and vascular function in diabetic and nondiabetic patients after balancing for coronary risk factors.MethodsWe studied 672 patients without overt coronary artery disease and normal myocardial perfusion on… read more here.
Keywords: nondiabetic patients; atherosclerotic burden; vascular function; diabetic patients ... See more keywords

Noninvasive evaluation of diabetic patients with high fasting blood glucose using DWI and BOLD MRI
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Abdominal Radiology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00261-020-02780-4
Abstract: To investigate the renal microstructure changes and hypoxia changes in type 2 diabetic patients and the relationship between them and glucose using both diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD MRI).… read more here.
Keywords: bold mri; group; diabetic patients; blood ... See more keywords

Imaging evaluation of the pancreas in diabetic patients
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Abdominal Radiology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00261-021-03340-0
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is becoming a global epidemic and its diagnosis and monitoring are based on laboratory testing which sometimes have limitations. The pancreas plays a key role in metabolism and is involved in the… read more here.
Keywords: imaging evaluation; pancreas diabetic; diabetic patients; patients imaging ... See more keywords

Improvement in Hyperglycemia Prevents Surgical Site Infection Irrespective of Insulin Therapy in Non-diabetic Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "World Journal of Surgery"
DOI: 10.1007/s00268-020-05371-y
Abstract: Background Intensive glycemic control is recommended to prevent surgical site infections (SSI). Our aim was to evaluate retrospectively the effect of improvement in hyperglycemia irrespective of insulin use on the incidence of SSI in non-diabetic… read more here.
Keywords: surgery; insulin therapy; diabetic patients; hyperglycemia ... See more keywords