
Impaired soft and hard callus formation during fracture healing in diet-induced obese mice as revealed by 3D contrast-enhanced computed tomography imaging.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Bone"
DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116008
Abstract: The impact of diabetes mellitus on bone fracture healing is clinically relevant as the patients experience delayed fracture healing. Even though efforts have been made to understand the detrimental effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus… read more here.
Keywords: fracture; diet induced; fracture healing; induced obese ... See more keywords

Optimized GIP analogs promote body weight lowering in mice through GIPR agonism not antagonism
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Molecular Metabolism"
DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.12.001
Abstract: Objective Structurally-improved GIP analogs were developed to determine precisely whether GIP receptor (GIPR) agonism or antagonism lowers body weight in obese mice. Methods A series of peptide-based GIP analogs, including structurally diverse agonists and a… read more here.
Keywords: weight lowering; gipr; mice; body weight ... See more keywords

Reduced calorie diet combined with NNMT inhibition establishes a distinct microbiome in DIO mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-03670-5
Abstract: Treatment with a nicotinamide N-methyltransferase inhibitor (NNMTi; 5-amino-1-methylquinolinium) combined with low-fat diet (LD) promoted dramatic whole-body adiposity and weight loss in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice, rapidly normalizing these measures to age-matched lean animals, while LD… read more here.
Keywords: age matched; mice; dio mice; distinct microbiome ... See more keywords

Abstract LB343: Antitumor and metabolomic evaluation of immune checkpoint inhibition in diet-induced obese mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Cancer Research"
DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.am2023-lb343
Abstract: Obesity is an epidemic in the Western world and a risk factor for at least 13 types of cancer. Cancer rates are rising for several obesity-related cancers, such as liver, pancreatic, thyroid, and uterine, as… read more here.
Keywords: growth; mice; dio mice; tumor ... See more keywords

Identification and Characterization of a Novel Insulin Sensitizer to Treat Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Diabetes"
DOI: 10.2337/db18-237-lb
Abstract: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) enhance insulin sensitivity and have efficacy for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). However, the use of TZDs, like rosiglitazone and pioglitazone, has been curtailed by significant side effects mediated via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor… read more here.
Keywords: insulin; msdc 5514; insulin sensitizer; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis ... See more keywords

Perturbation on gut microbiota impedes the onset of obesity in high fat diet-induced mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Endocrinology"
DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.795371
Abstract: High-calorie intake has become one of the most common causes of dietary obesity, which eventually develops into type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Microbiota, along with the length of the gastrointestinal tract, is related to metabolic… read more here.
Keywords: microbiota; gut microbiota; diet induced; obesity ... See more keywords

Glucose- and Bile Acid-Stimulated Secretion of Gut Hormones in the Isolated Perfused Intestine Is Not Impaired in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Endocrinology"
DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.884501
Abstract: Purpose Decreased circulating levels of food-intake-regulating gut hormones have been observed in type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, it is still unknown if this is due to decreased secretion from the gut mucosal cells or… read more here.
Keywords: glucose bile; dio mice; secretion; gut hormones ... See more keywords
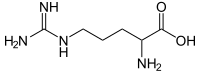
Beneficial Metabolic Effects of Praliciguat, a Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulator, in a Mouse Diet-Induced Obesity Model
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Pharmacology"
DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.852080
Abstract: Praliciguat is a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator that elicits hemodynamic, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic effects in preclinical models of metabolic dysfunction. We assessed the metabolic effects of praliciguat in a mouse diet-induced obesity (DIO) model housed… read more here.
Keywords: praliciguat soluble; model; mice; dio mice ... See more keywords

Taste-Driven Responsiveness to Fat and Sweet Stimuli in Mouse Models of Bariatric Surgery
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Biomedicines"
DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10040741
Abstract: A preferential consumption of healthier foods, low in fat and sugar, is often reported after bariatric surgery, suggesting a switch of taste-guided food choices. To further explore this hypothesis in well-standardized conditions, analysis of licking… read more here.
Keywords: surgery; taste; vsg; bariatric surgery ... See more keywords

Novel Site-Specific Fatty Chain-Modified GLP-1 Receptor Agonist with Potent Antidiabetic Effects
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Molecules"
DOI: 10.3390/molecules24040779
Abstract: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists have emerged as treatment options for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Here, we designed a high-throughput GLP-1R extracellular domain (ECD)-based system that enabled the screening of high-potency receptor-biased GLP-1R agonists… read more here.
Keywords: novel site; pep20; receptor; fatty chain ... See more keywords

Uroguanylin Improves Leptin Responsiveness in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Nutrients"
DOI: 10.3390/nu11040752
Abstract: The gastrointestinal-brain axis is a key mediator of the body weight and energy homeostasis regulation. Uroguanylin (UGN) has been recently proposed to be a part of this gut-brain axis regulating food intake, body weight and… read more here.
Keywords: dio mice; diet induced; induced obese; improves leptin ... See more keywords