
XPS characterization and E. Coli DNA degradation using functionalized Cu/TiO2 nanobiocatalysts
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Molecular Catalysis"
DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.02.010
Abstract: Abstract New copper compounds were proposed as alternative toxic agents against Nosocomial Infections (NI); in contrast with other copper complexes reported in the literature, they were inorganic nanobiocatalysts. The design of diverse Cu species such… read more here.
Keywords: characterization coli; coli dna; dna degradation; degradation using ... See more keywords

Structural insights into DNA degradation by human mitochondrial nuclease MGME1
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Nucleic Acids Research"
DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky855
Abstract: Abstract Mitochondrial nucleases play important roles in accurate maintenance and correct metabolism of mtDNA, the own genetic materials of mitochondria that are passed exclusively from mother to child. MGME1 is a highly conserved DNase that… read more here.
Keywords: dna; hsmgme1; dna degradation; structural insights ... See more keywords
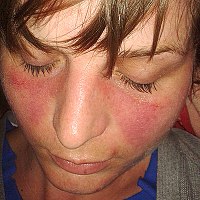
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and DNA Degradation and Elimination Defects
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Frontiers in Immunology"
DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01697
Abstract: Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that is characterized by the production of autoantibodies specific for components of the cell nucleus and that causes damage to body tissues and organs. The… read more here.
Keywords: degradation; dna; systemic lupus; lupus erythematosus ... See more keywords

Antifungal Potential of Synthetic Peptides against Cryptococcus neoformans: Mechanism of Action Studies Reveal Synthetic Peptides Induce Membrane–Pore Formation, DNA Degradation, and Apoptosis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Pharmaceutics"
DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081678
Abstract: Cryptococcus neoformans is a human-pathogenic yeast responsible for pneumonia and meningitis, mainly in patients immunocompromised. Infections caused by C. neoformans are a global health concern. Synthetic antimicrobial peptides (SAMPs) have emerged as alternative molecules to… read more here.
Keywords: dna degradation; apoptosis; synthetic peptides; antifungal potential ... See more keywords