
Impact of inappropriate empirical antibiotic treatment on clinical outcomes of urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli: a retrospective cohort study.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Journal of global antimicrobial resistance"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.05.016
Abstract: OBJECTIVE We aimed to determine the clinical impact of inappropriate empirical antibiotic treatment (IEAT) compared with appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment (AEAT) in hospitalised patients with urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli).… read more here.
Keywords: empirical antibiotic; antibiotic treatment; ieat; impact inappropriate ... See more keywords
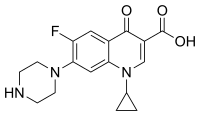
The cost-effectiveness of empirical antibiotic treatments for high-risk febrile neutropenic patients
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Medicine"
DOI: 10.1097/md.0000000000020022
Abstract: Supplemental Digital Content is available in the text read more here.
Keywords: high risk; antibiotic treatments; empirical antibiotic; cost effectiveness ... See more keywords

Outcomes of Single-Dose Empirical Antibiotic Treatment in Children With Suspected Sepsis Implemented in the Emergency Department
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Pediatric Emergency Care"
DOI: 10.1097/pec.0000000000002775
Abstract: Objectives Implementing a single-dose empirical antibiotic (SDEA) strategy at the emergency department (ED) in children with suspected sepsis may improve outcomes. We aim to evaluate the outcomes of the SDEA strategy for children with suspected… read more here.
Keywords: sepsis; single dose; dose empirical; empirical antibiotic ... See more keywords

Appropriateness of Empirical Antibiotic Therapy for Cervicitis and Urethritis Prescribed in the Emergency Department
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Hospital Pharmacy"
DOI: 10.1177/00185787221123219
Abstract: Objectives: Sexually transmitted infections are a prevalent global health care problem. Treatment guidelines have recently been updated as a result of antimicrobial resistance and public health trends. The aim of the study was to assess… read more here.
Keywords: emergency department; cervicitis urethritis; empirical antibiotic;

Empirical prescribing of penicillin G/V reduces risk of readmission of hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia in Norway: a retrospective observational study
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "BMC Pulmonary Medicine"
DOI: 10.1186/s12890-020-01188-6
Abstract: Background Norwegian guideline recommendations on first-line empirical antibiotic prescribing in hospitalised patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) are penicillin G/V in monotherapy, or penicillin G in combination with gentamicin (or cefotaxime) in severely ill patients. The… read more here.
Keywords: prescribing; readmission; empirical antibiotic; treatment ... See more keywords

Clinical Impact of Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Requiring Oxygen Therapy
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of Korean Medical Science"
DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e238
Abstract: Despite the low prevalence of secondary bacterial infection in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, most of them were administered antibiotic therapy empirically. However, the prognostic impact of empirical antibiotic therapy has not been evaluated. We… read more here.
Keywords: coronavirus disease; antibiotic therapy; therapy; empirical antibiotic ... See more keywords

Empirical Antibiotic Prescribing in Adult COVID-19 Inpatients over Two Years in Mexico
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Antibiotics"
DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11060764
Abstract: Background and Objectives: Empirical antibiotic prescribing in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been common even though bacterial coinfections are infrequent. The overuse of antibacterial agents may accelerate the antibiotic resistance crisis. We aimed… read more here.
Keywords: antibiotic prescribing; covid inpatients; adult covid; empirical antibiotic ... See more keywords