
Bioavailability of estrogenic compounds from sediment in the context of flood events evaluated by passive sampling.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Water research"
DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.020
Abstract: Studies worldwide have demonstrated through in vitro bioassays and chemical analysis that endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can accumulate in river sediments. However, remobilization of sediment-bound EDCs due to bioturbation or re-suspension during flood events remains poorly understood.… read more here.
Keywords: passive sampling; bioavailability; flood events; compounds sediment ... See more keywords
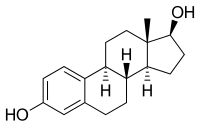
Secondary treatment phase of tertiary wastewater treatment works significantly reduces estrogenic load.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Water research"
DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117257
Abstract: Estrogenic compounds enter waterways via effluents from wastewater treatment works (WWTW), thereby indicating a potential risk to organisms inhabiting adjacent receiving waters. However, little is known about the loads or concentrations of estrogenic compounds that… read more here.
Keywords: phase; risk; treatment works; treatment ... See more keywords

Capture-SELEX of DNA Aptamers for Estradiol Specifically and Estrogenic Compounds Collectively.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Environmental science & technology"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.2c05808
Abstract: Estrogenic compounds such as estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), and 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) are serious environmental contaminants due to their potent biological activities. At least six selections were previously reported to obtain DNA aptamers for E2, highlighting… read more here.
Keywords: aptamers estradiol; estradiol specifically; estrogenic compounds; capture selex ... See more keywords

Removal of Estrogenic Compounds from Water Via Energy Efficient Sequential Electrocoagulation-Electrooxidation
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Environmental Engineering Science"
DOI: 10.1089/ees.2019.0335
Abstract: The purpose of this study was to investigate energy reduction using electrocoagulation (EC) followed by electrooxidation (EO) targeting initial removal of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) during EC a... read more here.
Keywords: removal estrogenic; electrooxidation; electrocoagulation; estrogenic compounds ... See more keywords