
Proteomic and metabonomic analysis uncovering Enterovirus A71 reprogramming host cell metabolic pathway
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "PROTEOMICS"
DOI: 10.1002/pmic.202200362
Abstract: Enterovirus A71 (EV71) infection can cause hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) and severe neurological complications in children. However, the biological processes regulated by EV71 remain poorly understood. Herein, proteomics and metabonomics studies were conducted… read more here.
Keywords: infection; glycolysis; enterovirus a71; ev71 infection ... See more keywords

Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides suppress EV71 infection via regulating antiviral response and inhibiting viral binding.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Antiviral research"
DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105021
Abstract: Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides (human LL-37 and mouse CRAMP) are mainly virucidal to enveloped virus. However, the effects and relative mechanism of LL-37 and CRAMP on non-enveloped virus are elusive. We herein found that CRAMP expression… read more here.
Keywords: response; cramp; infection; cathelicidin antimicrobial ... See more keywords

Harmine, a small molecule derived from natural sources, inhibits enterovirus 71 replication by targeting NF‐&kgr;B pathway
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "International Immunopharmacology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.050
Abstract: ABSTRACT Enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection of young children can cause neurological manifestations, which is mainly responsible for the fatality. Although a vaccine is recently available for preventing enterovirus 71 infection, its efficacy remains to be… read more here.
Keywords: ev71 infection; replication; ev71 replication; harmine ... See more keywords

Enterovirus 71 induces autophagy in mice via mTOR inhibition and ERK pathway activation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Life sciences"
DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119188
Abstract: AIMS Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is one of the main viruses that cause hand-foot-mouth disease; however, its pathogenic mechanism remains unclear. This study characterized the relationship between EV71 infection and autophagy in vivo and explored the… read more here.
Keywords: infection; inhibition; ev71 infection; pathway ... See more keywords

Mast cells contribute to Enterovirus 71 infection-induced pulmonary edema in neonatal mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Laboratory Investigation"
DOI: 10.1038/s41374-018-0075-y
Abstract: Enterovirus (EV) 71 infection has been widely acknowledged as the leading cause of severe hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD), which may rapidly lead to fatal pulmonary edema. In this study, we established a mouse… read more here.
Keywords: mast cells; infection; ev71 infection; pulmonary edema ... See more keywords

N-Acetyltransferase 8 Promotes Viral Replication by Increasing the Stability of Enterovirus 71 Nonstructural Proteins
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of Virology"
DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00119-22
Abstract: EV71 is one of the most common pathogens causing HFMD in young children, and some patients experience severe or fatal neurological consequences. To ensure efficient replication, the virus must hijack multiple host factors for its… read more here.
Keywords: ev71 replication; ev71 infection; acetyltransferase; infection ... See more keywords

Evaluation of the virucidal effects of rosmarinic acid against enterovirus 71 infection via in vitro and in vivo study
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Virology Journal"
DOI: 10.1186/s12985-019-1203-z
Abstract: BackgroundAlthough enterovirus 71 (EV71) is an important public health threat, especially in the Asia-Pacific region, there are still no effective drugs or vaccines to treat and prevent EV71 infection. Therefore, it is critical to develop… read more here.
Keywords: virucidal effects; rosmarinic acid; enterovirus; infection ... See more keywords
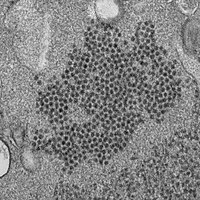
Muscle Tissue Damage and Recovery After EV71 Infection Correspond to Dynamic Macrophage Phenotypes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Frontiers in Immunology"
DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.648184
Abstract: Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is a positive single-stranded RNA virus from the enterovirus genus of the Picornaviridae family. Most young children infected with EV71 develop mild symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease, but some develop… read more here.
Keywords: recovery; infection; ev71 infection; macrophage ... See more keywords

Caspase-3 Inhibition Attenuates the Cytopathic Effects of EV71 Infection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Frontiers in Microbiology"
DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00817
Abstract: Previous studies demonstrate that human enterovirus 71 (EV71), a primary causative agent for hand, foot, and mouth disease, activates caspase-3 through the non-structural viral 3C protein to induce host cell apoptosis; however, until now it… read more here.
Keywords: caspase; inhibition; caspase caspase; ev71 infection ... See more keywords

MAVS-Based Reporter Systems for Real-Time Imaging of EV71 Infection and Antiviral Testing
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Viruses"
DOI: 10.3390/v15051064
Abstract: Enterovirus consists of a variety of viruses that could cause a wide range of illness in human. The pathogenesis of these viruses remains incompletely understood and no specific treatment is available. Better methods to study… read more here.
Keywords: reporter systems; based reporter; infection; mavs based ... See more keywords