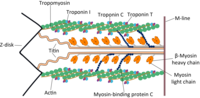
Inhibitors of the ubiquitin proteasome system block myofibril assembly in cardiomyocytes derived from chick embryos and human pluripotent stem cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Cytoskeleton"
DOI: 10.1002/cm.21697
Abstract: Details of sarcomeric protein assembly during de novo myofibril formation closely resemble myofibrillogenesis in skeletal and cardiac myocytes in birds, rodents, and zebrafish. The arrangement of proteins during myofibrillogenesis follows a three‐step process: beginning with… read more here.
Keywords: myofibril; ubiquitin proteasome; human cardiomyocytes; cardiomyocytes derived ... See more keywords
Iron deficiency impairs contractility of human cardiomyocytes through decreased mitochondrial function
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "European Journal of Heart Failure"
DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.1154
Abstract: Iron deficiency is common in patients with heart failure and associated with a poor cardiac function and higher mortality. How iron deficiency impairs cardiac function on a cellular level in the human setting is unknown.… read more here.
Keywords: human cardiomyocytes; iron deficiency; function; iron ... See more keywords

miR‐885 mediated cardioprotection against hypoxia/reoxygenation‐induced apoptosis in human cardiomyocytes via inhibition of PTEN and BCL2L11 and modulation of AKT/mTOR signaling
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of Cellular Physiology"
DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29460
Abstract: Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury could cause the enhanced cell apoptosis of cardiomyocytes, which is one of key contributors for the development of ischemic heart disease. Recent studies emphasized the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating cardiomyocyte… read more here.
Keywords: human cardiomyocytes; apoptosis; mtor signaling; mir 885 ... See more keywords

Astragaloside IV protects human cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by regulating miR-101a
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry"
DOI: 10.1007/s11010-020-03743-5
Abstract: Astragaloside IV (AS/IV) is one of the extracted components from the traditional Chinese medicine Astragalus which has been demonstrated to have potential capacity for anti-inflammation activity and for treating cardiovascular disease. Our purpose was to… read more here.
Keywords: hypoxia reoxygenation; human cardiomyocytes; injured cardiomyocytes; mir 101a ... See more keywords

Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) expression in diabetic and non-diabetic failing human cardiomyocytes.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Pharmacological research"
DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.4135653
Abstract: This study aimed at investigating the SGLT2 expression in human cardiomyocytes. Human studies evaluating cardiomyocyte SGLT2s expression are limited. To better clarify this issue, SGLT2 protein expression was assessed in human hearts of diabetic and… read more here.
Keywords: sglt2; non diabetic; diabetic non; human cardiomyocytes ... See more keywords

Cell-Target-Specific Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Empagliflozin: In Vitro Evidence in Human Cardiomyocytes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences"
DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.879522
Abstract: The antidiabetic sodium–glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) empagliflozin efficiently reduces heart failure (HF) hospitalization and cardiovascular death in type 2 diabetes (T2D). Empagliflozin-cardioprotection likely includes anti-inflammatory effects, regardless glucose lowering, but the underlying mechanisms… read more here.
Keywords: empagliflozin; cell target; human cardiomyocytes; anti inflammatory ... See more keywords

Potential Role of Lisinopril in Reducing Atherosclerotic Risk: Evidence of an Antioxidant Effect in Human Cardiomyocytes Cell Line
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Pharmacology"
DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.868365
Abstract: The cellular mechanisms involved in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (I/R) pathogenesis are complex but attributable to reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. ROS produced by coronary endothelial cells, blood cells (e.g., leukocytes and platelets), and cardiac myocytes… read more here.
Keywords: lisinopril; effect; oxidative stress; human cardiomyocytes ... See more keywords

Expression of atrial-fetal light chains in cultured human cardiomyocytes after chemical ischemia-reperfusion injury
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Molecular Medicine Reports"
DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12410
Abstract: Atrial light chains (ALC1) are naturally present in adult heart atria, while ventricular light chains (VLC1) are predominant in ventricles. Degradation of VLC1 and re-expression of ALC1 in heart ventricles are associated with heart disorders… read more here.
Keywords: human cardiomyocytes; heart; light; expression ... See more keywords

MiRNA-615-3p Alleviates Oxidative Stress Injury of Human Cardiomyocytes Via PI3K/Akt Signaling by Targeting MEF2A
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Anatolian Journal of Cardiology"
DOI: 10.5152/anatoljcardiol.2021.901
Abstract: Background Myocardial infarction, a coronary heart disease, is a serious hazard to human health. Cardiomyocyte oxidative stress and apoptosis have been considered as the main causes of myocardial infarction. Here, we aimed to investigate the… read more here.
Keywords: apoptosis; mef2a; oxidative stress; human cardiomyocytes ... See more keywords