
A Human‐Specific De Novo Gene Promotes Cortical Expansion and Folding
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Advanced Science"
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204140
Abstract: Newly originated de novo genes have been linked to the formation and function of the human brain. However, how a specific gene originates from ancestral noncoding DNAs and becomes involved in the preexisting network for… read more here.
Keywords: gene; gene promotes; specific novo; human specific ... See more keywords
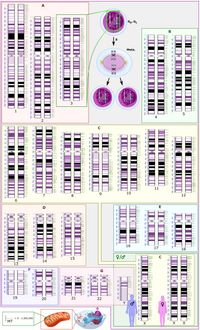
Novel gene function and regulation in neocortex expansion.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Current opinion in cell biology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.11.008
Abstract: The expansion of the neocortex during human evolution is due to changes in our genome that result in increased and prolonged proliferation of neural stem and progenitor cells during neocortex development. Three principal types of… read more here.
Keywords: expansion; human specific; novel gene; function ... See more keywords

Genome-wide analysis of pseudogenes reveals HBBP1's human-specific essentiality in erythropoiesis and implication in β-thalassemia.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Developmental cell"
DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.12.019
Abstract: The human genome harbors 14,000 duplicated or retroposed pseudogenes. Given their functionality as regulatory RNAs and low conservation, we hypothesized that pseudogenes could shape human-specific phenotypes. To test this, we performed co-expression analyses and found… read more here.
Keywords: genome wide; thalassemia; wide analysis; analysis pseudogenes ... See more keywords

Human-specific approaches to brain research for the 21st century: a South American perspective.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Drug discovery today"
DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.06.001
Abstract: The 21st century paradigm in toxicology, which emphasizes mechanistic understanding and species-relevant modeling of human biology and pathophysiology, is gaining traction in the wider biosciences through a global workshop series organized by the BioMed21 Collaboration.… read more here.
Keywords: research; brain research; south american; 21st century ... See more keywords

Evidence for opposing selective forces operating on human-specific duplicated TCAF genes in Neanderthals and humans
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Nature Communications"
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25435-4
Abstract: TRP channel-associated factor 1/2 (TCAF1/TCAF2) proteins antagonistically regulate the cold-sensor protein TRPM8 in multiple human tissues. Understanding their significance has been complicated given the locus spans a gap-ridden region with complex segmental duplications in GRCh38.… read more here.
Keywords: selective forces; forces operating; opposing selective; evidence opposing ... See more keywords

A human-specific switch of alternatively spliced AFMID isoforms contributes to TP53 mutations and tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Genome research"
DOI: 10.1101/gr.227181.117
Abstract: Pre-mRNA splicing can contribute to the switch of cell identity that occurs in carcinogenesis. Here, we analyze a large collection of RNA-seq data sets and report that splicing changes in hepatocyte-specific enzymes, such as AFMID… read more here.
Keywords: recurrence; afmid isoforms; switch; switch alternatively ... See more keywords

Transcriptional fates of human-specific segmental duplications in brain.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Genome research"
DOI: 10.1101/gr.237610.118
Abstract: Despite the importance of duplicate genes for evolutionary adaptation, accurate gene annotation is often incomplete, incorrect, or lacking in regions of segmental duplication. We developed an approach combining long-read sequencing and hybridization capture to yield… read more here.
Keywords: full length; segmental duplications; specific segmental; human specific ... See more keywords

Exploiting species specificity to understand the tropism of a human-specific toxin
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Science Advances"
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aax7515
Abstract: Overcoming the species specificity of the MRSA toxin LukAB with a novel mouse model establishes a role for LukAB in vivo. Many pathogens produce virulence factors that are specific toward their natural host. Clinically relevant… read more here.
Keywords: species specificity; lukab; cd11b; toxin ... See more keywords

A Versatile Human Intestinal Organoid-Derived Epithelial Monolayer Model for the Study of Enteric Pathogens
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Microbiology Spectrum"
DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00003-21
Abstract: While traditional laboratory techniques and animal models have provided valuable knowledge in discerning virulence mechanisms of enteric pathogens, the complexity of the human gastrointestinal tract has hindered our understanding of physiologically relevant, human-specific interactions and,… read more here.
Keywords: human intestinal; model; human specific; organoid derived ... See more keywords

Abstract 5194: Humanized PD-1 knock-in mice as a model system for combination therapies with human specific PD-1 therapeutics
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Cancer Research"
DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.am2023-5194
Abstract: Checkpoint inhibitor treatment has become a common therapy for various cancer types. As an escape mechanism, tumor cells express PD-L1 on their surface, as a ligand for PD-1 with players of the immune system (such… read more here.
Keywords: system; combination therapies; c57bl; human specific ... See more keywords

Human-specific mutations in VMAT1 confer functional changes and multi-directional evolution in the regulation of monoamine circuits
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "BMC Evolutionary Biology"
DOI: 10.1186/s12862-019-1543-8
Abstract: BackgroundNeurochemicals like serotonin and dopamine play crucial roles in human cognitive and emotional functions. Vesicular monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) transports monoamine neurotransmitters, and its variant (136Thr) is associated with various psychopathological symptoms and reduced monoamine… read more here.
Keywords: evolution; monoamine uptake; functional changes; vmat1 ... See more keywords