
Cognitive deficits associated with impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Diabetologia"
DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4233-3
Abstract: Aims/hypothesisThe aim of this study was to compare cognitive function in adults with type 1 diabetes who have impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia with those who have normal awareness of hypoglycaemia. A putative association was sought… read more here.
Keywords: hypoglycaemia; impaired awareness; type diabetes; awareness hypoglycaemia ... See more keywords

Impaired Awareness of Problem and Pathological Gambling: A Review
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of Gambling Studies"
DOI: 10.1007/s10899-019-09926-0
Abstract: Although well-recognized and clinically relevant, impaired awareness of problem and pathological gambling (IAPPG) is a poorly understood phenomenon that contributes to treatment denial and negative clinical and social outcomes. In this study, we aimed to… read more here.
Keywords: awareness; problem pathological; impaired awareness; awareness problem ... See more keywords
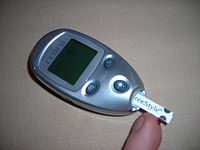
Prevalence of severe hypoglycemia in a cohort of patients with type 1 diabetes.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Endocrinologia, diabetes y nutricion"
DOI: 10.1016/j.endinu.2020.01.002
Abstract: INTRODUCTION Hypoglycemia is the major limiting factor in the glycemic management of type 1 diabetes. Severe hypoglycemia puts patients at risk of injury and death. Recurrent hypoglycemia leads to impaired awareness of hypoglycemia and this… read more here.
Keywords: awareness hypoglycemia; hypoglycemia; impaired awareness; prevalence severe ... See more keywords

Real life evidence that impaired awareness of hypoglycemia persists for years in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of diabetes and its complications"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2018.08.015
Abstract: AIMS To determine if impaired awareness of hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes persists over time and to assess if continuous glucose monitoring use was associated with improved awareness of hypoglycemia in our population.… read more here.
Keywords: patients type; awareness hypoglycemia; hypoglycemia; impaired awareness ... See more keywords

RD Lawrence Lecture 2015 Old habits are hard to break: lessons from the study of hypoglycaemia
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Diabetic Medicine"
DOI: 10.1111/dme.13277
Abstract: Despite the introduction of newer technologies and improved insulin formulations, recurrent hypoglycaemia continues to affect the lives of many people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Developing strategies or therapies designed to prevent or… read more here.
Keywords: hypoglycaemia; impaired awareness; lawrence lecture; 2015 old ... See more keywords

Impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in women with type 1 diabetes in pregnancy: Hypoglycaemia fear, glycaemic and pregnancy outcomes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Diabetic Medicine"
DOI: 10.1111/dme.14789
Abstract: To examine maternal fear of hypoglycaemia, glycaemia and pregnancy outcomes in women with impaired and normal awareness of hypoglycaemia. read more here.
Keywords: awareness hypoglycaemia; hypoglycaemia women; pregnancy outcomes; pregnancy ... See more keywords

Fall in prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in individuals with type 1 diabetes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Diabetic Medicine"
DOI: 10.1111/dme.15042
Abstract: Impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia (IAH) has been reported to affect up to a third of people with type 1 diabetes. Whether the increased use of sensor technology has changed its prevalence remains unknown. The aim… read more here.
Keywords: impaired awareness; prevalence; awareness hypoglycaemia; type diabetes ... See more keywords

Short duration of focal onset awareness and impaired awareness seizure are characteristic features of epilepsy in elderly patients
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment"
DOI: 10.2147/ndt.s179720
Abstract: Purpose Diagnosing epilepsy in the elderly population can be difficult due to mimicking symptoms. Furthermore, epileptic symptoms can also be masked by various symptoms. We hypothesized that elderly patients with epilepsy exhibit specific clinical features… read more here.
Keywords: duration; impaired awareness; epilepsy group; group ... See more keywords

194-OR: Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia and Maternal/Neonatal Outcomes in the CONCEPTT Trial
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Diabetes"
DOI: 10.2337/db20-194-or
Abstract: Background: Patients with diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycemia (IAH) are at increased risk of severe hypoglycemia (SH). IAH is increased during pregnancy. To date, maternal and neonatal outcomes of pregnant women with hypoglycemia unawareness… read more here.
Keywords: trial; awareness hypoglycemia; hypoglycemia; impaired awareness ... See more keywords

Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression Are Independently Associated With Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Diabetes care"
DOI: 10.2337/dc21-2482
Abstract: OBJECTIVE We tested the hypothesis that impaired awareness of hypoglycemia (IAH) is independently associated with symptoms of anxiety and depression in type 1 diabetes. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS In this cross-sectional observational study in 950… read more here.
Keywords: anxiety depression; independently associated; type diabetes; anxiety ... See more keywords

Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Report of An NIDDK Workshop in October 2021.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Diabetes care"
DOI: 10.2337/dc22-1242
Abstract: Hypoglycemia remains a limiting factor in the optimal treatment of type 1 diabetes. Repeated episodes of hypoglycemia result in impaired awareness of subsequent hypoglycemic events, inducing a vicious feed-forward cycle and increasing the risk of… read more here.
Keywords: october 2021; workshop october; awareness hypoglycemia; type diabetes ... See more keywords