
LC-MS proteomic profiling of Caco-2 human intestinal cells exposed to the copper-chelating agent, triethylenetetramine: A preliminary study.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Biochemical and biophysical research communications"
DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.138
Abstract: Homeostasis of metal micronutrients such as copper is tightly regulated to ensure deficiency does not occur while restricting damage resulting from excess accumulation. Using LC-MS the effect on the proteome of intestinal Caco-2 cells of exposure… read more here.
Keywords: copper; study; intestinal cells; proteomic profiling ... See more keywords

Escherichia coli K12: An evolving opportunistic commensal gut microbe distorts barrier integrity in human intestinal cells.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Microbial pathogenesis"
DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103545
Abstract: Commensal enteric microbes under specific conditions viz. immunocompromised system, altered microbiota or uncompetitive niche induce their otherwise dormant pathogenic phenotype to distort host cellular functioning. Here we investigate how under in vitro environment established by… read more here.
Keywords: gut microbe; coli k12; commensal gut; intestinal cells ... See more keywords
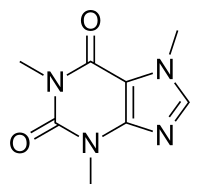
Extract of Unifloral Camellia sinensis L. Pollen Collected by Apis mellifera L. Honeybees Exerted Inhibitory Effects on Glucose Uptake and Transport by Interacting with Glucose Transporters in Human Intestinal Cells.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Journal of agricultural and food chemistry"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07160
Abstract: Bee pollen possesses potential hypoglycemic effects but its inhibitory mechanisms on glucose absorption and transportation in intestinal cells still need to be clarified. Here, we determined the inhibitory effects of bee pollen extract originating from… read more here.
Keywords: inhibitory effects; glucose uptake; intestinal cells; uptake transport ... See more keywords

Differential effects of Clostridium difficile toxins on ion secretion and cell integrity in human intestinal cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Pediatric Research"
DOI: 10.1038/s41390-019-0365-0
Abstract: BackgroundToxin A (TcdA), toxin B (TcdB), and binary toxin (CDT) produced by Clostridium difficile (CD) are thought to play a key role in inducing diarrhea. The aim of this study was to investigate the individual… read more here.
Keywords: clostridium difficile; secretion; tcda; intestinal cells ... See more keywords

Food-borne Lactiplantibacillus plantarum protect normal intestinal cells against inflammation by modulating reactive oxygen species and IL-23/IL-17 axis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73201-1
Abstract: Food-associated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (Lpb. plantarum) strains, previously classified as Lactobacillus plantarum, are a promising strategy to face intestinal inflammatory diseases. Our study was aimed at clarifying the protective role of food-borne Lpb. plantarum against inflammatory… read more here.
Keywords: lpb plantarum; plantarum; lactiplantibacillus plantarum; intestinal cells ... See more keywords

Coculture with hiPS-derived intestinal cells enhanced human hepatocyte functions in a pneumatic-pressure-driven two-organ microphysiological system
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84861-y
Abstract: Examining intestine–liver interactions is important for achieving the desired physiological drug absorption and metabolism response in in vitro drug tests. Multi-organ microphysiological systems (MPSs) constitute promising tools for evaluating inter-organ interactions in vitro. For coculture… read more here.
Keywords: pneumatic pressure; organ microphysiological; derived intestinal; intestinal cells ... See more keywords

Celiac Diasease–associated lncRNA Named HCG14 Regulates NOD1 Expression in Intestinal Cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition"
DOI: 10.1097/mpg.0000000000001970
Abstract: Objective: The aim of the study is to identify additional celiac disease associated loci in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) independent from classical HLA risk alleles (HLA-DR3-DQ2) and to characterize their potential functional impact in… read more here.
Keywords: hcg14; nod1 expression; intestinal cells; celiac disease ... See more keywords

Natural variation in the roles of C. elegans autophagy components during microsporidia infection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "PLoS ONE"
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216011
Abstract: Natural genetic variation can determine the outcome of an infection, and often reflects the co-evolutionary battle between hosts and pathogens. We previously found that a natural variant of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans from Hawaii (HW)… read more here.
Keywords: variation; natural variation; infection; inside intestinal ... See more keywords

Adhesion Ability and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Malaysian Fermented Fish (Pekasam) on HT-29 and CCD-18CO Intestinal Cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Sains Malaysiana"
DOI: 10.17576/jsm-2018-4710-15
Abstract: Bacterial adhesion to host cells is the most important probiotic character. However, the adhesion of probiotic should not affect the viability of the host cells. In this study, Lactobacillus plantarum strain L8, Lactobacillus plantarum strain… read more here.
Keywords: microscopy; adhesion; ccd 18co; intestinal cells ... See more keywords
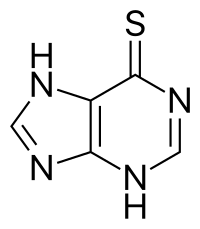
PACSIN2 as a modulator of autophagy and mercaptopurine cytotoxicity: mechanisms in lymphoid and intestinal cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Life Science Alliance"
DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202201610
Abstract: This study evaluates the role of PACSIN2 in autophagy modulation and its impact on mercaptopurine cytotoxicity in lymphoid and intestinal models. PACSIN2 variants are associated with gastrointestinal effects of thiopurines and thiopurine methyltransferase activity through… read more here.
Keywords: mercaptopurine cytotoxicity; cytotoxicity; intestinal cells; pacsin2 ... See more keywords

Three Layers of Intestinal γδ T Cells Talk Different Languages With the Microbiota
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Immunology"
DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849954
Abstract: The mucosal surfaces of our body are the main contact site where the immune system encounters non-self molecules from food-derived antigens, pathogens, and symbiotic bacteria. γδ T cells are one of the most abundant populations… read more here.
Keywords: intestinal cells; different languages; talk different; three layers ... See more keywords