Sustained effects of rapidly acting antidepressants require BDNF-dependent MeCP2 phosphorylation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Nature neuroscience"
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-021-00868-8
Abstract: The rapidly acting antidepressants ketamine and scopolamine exert behavioral effects that can last from several days to more than a week in some patients. The molecular mechanisms underlying the maintenance of these antidepressant effects are… read more here.
Keywords: ketamine scopolamine; rapidly acting; acting antidepressants; mecp2 phosphorylation ... See more keywords

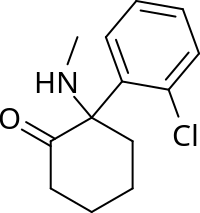
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Rapid-Acting Antidepressants Ketamine and Scopolamine
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Current Neuropharmacology"
DOI: 10.2174/1570159x14666160309114549
Abstract: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a prevalent neuropsychiatric disease that causes profound social and economic burdens. The impact of MDD is compounded by the limited therapeutic efficacy and delay of weeks to months of currently… read more here.
Keywords: ketamine scopolamine; molecular cellular; cellular mechanisms; rapid acting ... See more keywords