
A Brownian Ratchet Model Explains the Biased Sidestepping of Single-Headed Kinesin-3 KIF1A.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Biophysical journal"
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.05.011
Abstract: The kinesin-3 motor KIF1A is involved in long-ranged axonal transport in neurons. To ensure vesicular delivery, motors need to navigate the microtubule lattice and overcome possible roadblocks along the way. The single-headed form of KIF1A… read more here.
Keywords: kif1a; single headed; microtubule lattice; motor ... See more keywords

De novo mutations in KIF1A-associated neuronal disorder (KAND) dominant-negatively inhibit motor activity and axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America"
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2113795119
Abstract: KIF1A is a kinesin superfamily molecular motor that transports synaptic vesicle precursors in axons. Mutations in Kif1a lead to a group of neuronal diseases called KIF1A-associated neuronal disorder (KAND). KIF1A forms a homodimer and KAND… read more here.
Keywords: synaptic vesicle; disease; kif1a; kand ... See more keywords
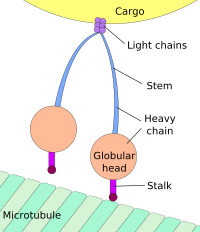
Pseudorabies Virus Infection Accelerates Degradation of the Kinesin-3 Motor KIF1A
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of Virology"
DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01934-19
Abstract: Pseudorabies virus (PRV) is an alphaherpesvirus related to human pathogens herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 and varicella-zoster virus. Alphaherpesviruses are neuroinvasive pathogens that establish lifelong latent infections in the host peripheral nervous system (PNS).… read more here.
Keywords: kinesin; transport; infection; motor ... See more keywords

The Novel KIF1A Missense Variant (R169T) Strongly Reduces Microtubule Stimulated ATPase Activity and Is Associated With NESCAV Syndrome
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Frontiers in Neuroscience"
DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.618098
Abstract: KIF1A is a microtubule-dependent motor protein responsible for fast anterograde transport of synaptic vesicle precursors in neurons. Pathogenic variants in KIF1A have been associated with a wide spectrum of neurological disorders. Here, we report a… read more here.
Keywords: microtubule; kif1a; variant; r169t ... See more keywords

Dodecyl creatine ester improves cognitive function and identifies key protein drivers including KIF1A and PLCB1 in a mouse model of creatine transporter deficiency
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience"
DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1118707
Abstract: Creatine transporter deficiency (CTD), a leading cause of intellectual disability is a result of the mutation in the gene encoding the creatine transporter SLC6A8, which prevents creatine uptake into the brain, causing mental retardation, expressive… read more here.
Keywords: plcb1; creatine; kif1a; brain ... See more keywords