
Shape Control of Lotus Leaf Induced by Surface Submillimeter Texture
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Advanced Materials Interfaces"
DOI: 10.1002/admi.202000040
Abstract: Automatic slant of lotus leaf achieving self‐motive unidirectional fluid transport is significant for self‐cleaning, decreasing load, enhancing respiration, and receiving more sunlight, which is the consequence of natural evolution. In this study, the mechanism of… read more here.
Keywords: lotus leaf; shape control; submillimeter; surface ... See more keywords

Facile and Effective Preparation of the Lotus Leaf-based Adsorbent by Exposing Cellulose Nanocrystal for Waste Water Treatment and Air Purification
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Fibers and Polymers"
DOI: 10.1007/s12221-020-9264-6
Abstract: One substantial plant waste, lotus leave was fabricated into lotus leave powder with different diameters by ball milling. The surface morphology, chemical composition, particle size, porosity parameters, crystal structure, and wettability of lotus leaf powders… read more here.
Keywords: lotus leaf; waste; spectroscopy; microscopy ... See more keywords

Lotus leaf inspired antiadhesive and antibacterial gauze for enhanced infected dermal wound regeneration
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Chemical Engineering Journal"
DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126202
Abstract: Abstract Gauze is the leading dressing for wound management. However, infection and tissue adhesion pose serious challenges to the application of gauzes. Herein, inspired by the self-cleaning property of lotus leaf, we develop a novel… read more here.
Keywords: lotus leaf; antibacterial gauze; gauze; antiadhesive antibacterial ... See more keywords

A lotus-leaf-like SiO2 superhydrophobic bamboo surface based on soft lithography
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects"
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.02.043
Abstract: Abstract Biological microstructures have been a source of inspiration for scientific researchers and artists. In this paper, the microstructure of the lotus leaf was replicated on the bamboo surfaces by soft lithography, using a fresh… read more here.
Keywords: lotus leaf; bamboo; surface; leaf like ... See more keywords

Effect of enzyme-assisted extraction on the physicochemical properties and bioactive potential of lotus leaf polysaccharides.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "International journal of biological macromolecules"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.252
Abstract: Lotus leaf polysaccharides were extracted by enzyme-assisted extraction using α-amylase (LLEP-A), cellulose (LLEP-C), pectinase (LLEP-P) or protease (LLEP-PR). Their physicochemical properties and immunostimulatory activities were compared with those of hot-water extracted polysaccharides (LLWP). HPAEC-PDA and… read more here.
Keywords: leaf polysaccharides; lotus leaf; enzyme assisted; llep ... See more keywords

Vascular cell behavior on heparin-like polymers modified silicone surfaces: The prominent role of the lotus leaf-like topography.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Journal of colloid and interface science"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.06.100
Abstract: Vascular cell behavior on material surfaces, such as heparin-like polymers, can be affected by the surface chemical composition and surface topological structure. In this study, the effects of heparin-like polymers and lotus leaf-like topography on… read more here.
Keywords: topography; lotus leaf; leaf like; heparin like ... See more keywords

A sensitive and reproducible SERS sensor based on natural lotus leaf for paraquat detection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Microchemical Journal"
DOI: 10.1016/j.microc.2020.105728
Abstract: Abstract A facile and green approach of using natural lotus leaf as a superhydrophobic platform was proposed for sensitive and reproducible surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) detection. The surface of a lotus leave provides hydrophobic… read more here.
Keywords: detection; sensitive reproducible; sers sensor; lotus leaf ... See more keywords

Biomimetic fabrication of micro-/nanostructure on polypropylene surfaces with high dynamic superhydrophobic stability
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Materials Today Communications"
DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.04.005
Abstract: Abstract Recently, the biomimetic replication of micro-/nanostructure present on lotus leaves has attracted great interest. Unfortunately, the nanostructure on the surfaces of lotus leaves, which play a critical role in making them superhydrophobic and self-cleaning,… read more here.
Keywords: lotus; polypropylene surfaces; lotus leaf; micro nanostructure ... See more keywords
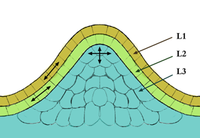
A lotus leaf based random laser
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Organic Electronics"
DOI: 10.1016/j.orgel.2019.03.032
Abstract: Abstract Random lasing in a lotus leaf, with a wide tunable spectrum from planar liquid waveguide gain channels is described. The lotus leaf shows multiple scattering from the micro-papilla and nanoscale coralloid tomentum on its… read more here.
Keywords: leaf based; based random; lotus leaf; random laser ... See more keywords

Superefficient and robust polymer coating for bionic manufacturing of superwetting surfaces with “rose petal effect” and “lotus leaf effect”
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Progress in Organic Coatings"
DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.106090
Abstract: Abstract Mimicking the superwetting behaviors of nature creatures is advantageous for the development of multifunctional surfaces. Superhydrophobic surfaces are desired for applications such as self-cleaning, drag reduction, anti-staining, anti-corrosion, oil-water separation, etc. Herein, a superefficient… read more here.
Keywords: petal effect; lotus leaf; leaf effect; rose petal ... See more keywords

Rhamnogalacturonan I-Enriched Pectin, Flavonoids, and Alkaloids from Lotus Leaf Infusion in Regulating Glycolipid Absorption and Metabolism: Isolation, In Vitro Bioactivity Verification, and Structural Characterization.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Journal of agricultural and food chemistry"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02522
Abstract: Lotus leaf is effective in regulating glycolipid absorption and metabolism, but the roles of small-molecule compounds and polysaccharides are unknown. In this study, the small-molecule compounds including flavonoids, alkaloids, and polysaccharides were gradually isolated from… read more here.
Keywords: glycolipid absorption; lotus leaf; absorption metabolism; regulating glycolipid ... See more keywords