
Coordination of Autophagosome–Lysosome Fusion by Atg8 Family Members
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Current Biology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.034
Abstract: Macroautophagy is a conserved intracellular lysosomal degradative pathway, vital for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. It is characterized by double-membrane vesicles called autophagosomes, which sequester the cytoplasmic material destined for lysosomal turnover. In a final step,… read more here.
Keywords: lysosome fusion; fusion atg8; coordination autophagosome; family ... See more keywords

The IAP family member BRUCE regulates autophagosome–lysosome fusion
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Nature Communications"
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-02823-x
Abstract: Autophagy has an important role in cellular homeostasis by degrading and recycling cytotoxic components. Ubiquitination is known to target cargoes for autophagy; however, key components of this pathway remain elusive. Here we performed an RNAi… read more here.
Keywords: lysosome fusion; iap family; bruce; fusion ... See more keywords

Augmenting ATG14 alleviates atherosclerosis and inhibits inflammation via promotion of autophagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Autophagy"
DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1909833
Abstract: Dysfunction of macroautophagy/autophagy in macrophages contributes to atherosclerosis. Impaired autophagy-lysosomal degradation system leads to lipid accumulation, facilitating atherosclerotic plaque. ATG14 is an essential regulator for the fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes. Whether ATG14 plays a… read more here.
Keywords: lysosome fusion; inflammation; autophagosome lysosome; augmenting atg14 ... See more keywords
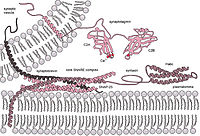
MTOR-mediates hepatic lipid metabolism through an autophagic SNARE complex
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Autophagy"
DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2037853
Abstract: ABSTRACT The STX17-SNAP29-VAMP8 SNARE complex mediates autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Our recent study showed that MTOR directly phosphorylates VAMP8ʹs T48 residue in nutrient-rich conditions. Phosphorylated VAMP8 inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion by blocking STX17-SNAP29-VAMP8 SNARE complex formation. Our study… read more here.
Keywords: lysosome fusion; snare; autophagosome lysosome; lipid metabolism ... See more keywords

Acetylation of SCFD1 regulates SNARE complex formation and autophagosome-lysosome fusion
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Autophagy"
DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2064624
Abstract: ABSTRACT SCFD1 (sec1 family domain containing 1) was recently shown to function in autophagosome-lysosome fusion, and multiple studies have demonstrated the regulatory impacts of acetylation (a post-translational modification) on macroautophagy/autophagy. Here, we demonstrate that both… read more here.
Keywords: lysosome fusion; acetylation; scfd1; autophagosome lysosome ... See more keywords

CLEC18A Impairs Phagocytosis by Reducing FcγRIIA Expression and Arresting Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Microbiology Spectrum"
DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02903-22
Abstract: During infection, the host immune system produces cellular factors to protect against pathogen invasion. However, when the immune response overreacts and there is dysregulated cytokine homeostasis, autoimmunity occurs following an infection. ABSTRACT Mixed cryoglobulinemia (MC)… read more here.
Keywords: lysosome fusion; autophagosome lysosome; infection; riia expression ... See more keywords

The Phagosome–Lysosome Fusion Is the Target of a Purified Quillaja saponin Extract (PQSE) in Reducing Infection of Fish Macrophages by the Bacterial Pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Antibiotics"
DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10070847
Abstract: Piscirickettsia salmonis, the etiological agent of Piscirickettsiosis, is a Gram-negative and facultative intracellular pathogen that has affected the Chilean salmon industry since 1989. The bacterium is highly aggressive and can survive and replicate within fish… read more here.
Keywords: pathogen; lysosome fusion; fish macrophages; piscirickettsia salmonis ... See more keywords