
Carbon flux to growth or polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis under microaerophilic conditions is affected by fatty acid chain-length in Pseudomonas putida LS46
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00253-018-9055-9
Abstract: Economical production of medium-chain length polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHA) is dependent on efficient cultivation processes. This work describes growth and mcl-PHA synthesis characteristics of Pseudomonas putida LS46 when grown on medium-chain length fatty acids (octanoic acid) and… read more here.
Keywords: chain length; growth; mcl pha; pha ... See more keywords
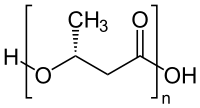
Binary polyhydroxyalkanoate systems for soft tissue engineering.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Acta biomaterialia"
DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.02.027
Abstract: Progress in tissue engineering is dependent on the availability of suitable biomaterials. In an effort to overcome the brittleness of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), P(3HB), a natural biodegradable polyester, and widen its biomedical applications, plasticising of P(3HB) with… read more here.
Keywords: tissue engineering; polyhydroxyalkanoate; mcl pha; pha ... See more keywords

Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas mendocina NK-01 for enhanced production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates with enriched content of the dominant monomer.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "International journal of biological macromolecules"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.044
Abstract: In this study, six genes involved in β-oxidation pathway of P. mendocina NK-01 were deleted to construct mutant strains NKU-∆β1 and NKU-∆β5. Compared with the wild strain NKU, the mcl-PHA titers of NKU-∆β5 were respectively… read more here.
Keywords: mendocina; metabolic engineering; pha; dominant monomer ... See more keywords

Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for increased polyhydroxyalkanoate production from lignin
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Microbial Biotechnology"
DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13481
Abstract: Microbial conversion offers a promising strategy for overcoming the intrinsic heterogeneity of the plant biopolymer, lignin. Soil microbes that natively harbour aromatic‐catabolic pathways are natural choices for chassis strains, and Pseudomonas putida KT2440 has emerged… read more here.
Keywords: production; metabolic engineering; lignin; pseudomonas putida ... See more keywords

Reconstruction and optimization of a Pseudomonas putida-Escherichia coli microbial consortium for mcl-PHA production from lignocellulosic biomass
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology"
DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1023325
Abstract: The demand for non-petroleum-based, especially biodegradable plastics has been on the rise in the last decades. Medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate (mcl-PHA) is a biopolymer composed of 6–14 carbon atoms produced from renewable feedstocks and has become the… read more here.
Keywords: production; consortium; mcl pha; microbial consortium ... See more keywords

Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Extracellular Products Using Pseudomonas Corrugata and P. Mediterranea: A Review
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Bioengineering"
DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering6040105
Abstract: Some strains of Pseudomonas corrugata (Pco) and P. mediterranea (Pme) efficiently synthesize medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates elastomers (mcl-PHA) and extracellular products on related and unrelated carbon sources. Yield and composition are dependent on the strain, carbon source,… read more here.
Keywords: production; pha; extracellular products; pseudomonas corrugata ... See more keywords

Polyenes in Medium Chain Length Polyhydroxyalkanoate (mcl-PHA) Biopolymer Microspheres with Reduced Toxicity and Improved Therapeutic Effect against Candida Infection in Zebrafish Model
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Pharmaceutics"
DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040696
Abstract: Immobilizing antifungal polyenes such as nystatin (Nys) and amphotericin B (AmB) into biodegradable formulations is advantageous compared to free drug administration providing sustained release, reduced dosing due to localized targeting and overall reduced systemic drug… read more here.
Keywords: mcl pha; toxicity; zebrafish model; chain length ... See more keywords