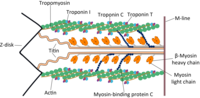
Zinc protects against cadmium-induced toxicity in neonatal murine engineered cardiac tissues via metallothionein-dependent and independent mechanisms
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Acta Pharmacologica Sinica"
DOI: 10.1038/s41401-019-0320-y
Abstract: Cadmium (Cd) is a nonessential heavy metal and a prevalent environmental toxin that has been shown to induce significant cardiomyocyte apoptosis in neonatal murine engineered cardiac tissues (ECTs). In contrast, zinc (Zn) is a potent… read more here.
Keywords: neonatal murine; murine engineered; engineered cardiac; toxicity ... See more keywords

Neonatal Murine Engineered Cardiac Tissue Toxicology Model: Impact of Metallothionein Overexpression on Cadmium-Induced Injury
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Toxicological Sciences"
DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy177
Abstract: Engineered cardiac tissues (ECTs) serve as robust in vitro models to study human cardiac diseases including cardiac toxicity assays due to rapid structural and functional maturation and the ability to vary ECT composition. Metallothionein (MT)… read more here.
Keywords: overexpression; neonatal murine; engineered cardiac; toxicity ... See more keywords