
Analysis of Growth, Nutritional Status and Hospital Visitation Scores Associated with Reflux After Nissen Fundoplication in Neurologically Impaired Children with Gastroesophageal Reflux
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "World Journal of Surgery"
DOI: 10.1007/s00268-017-4276-0
Abstract: Background Neurologically impaired children (NIC) often experience swallowing difficulties and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Although these conditions could place children in a state of poor nutritional status and prevent them from thriving, there is insufficient… read more here.
Keywords: status; fundoplication; nutritional status; neurologically impaired ... See more keywords

Laparoscopic gastroesophageal dissociation in neurologically impaired children with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of pediatric surgery"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.10.010
Abstract: PURPOSE Neurologically impaired children with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are a challenging group of patients. We theorized that a laparoscopic gastroesophageal dissociation (LGED) may decrease reflux-related readmissions and healthcare visits, and improve quality of… read more here.
Keywords: laparoscopic gastroesophageal; neurologically impaired; reflux disease; impaired children ... See more keywords
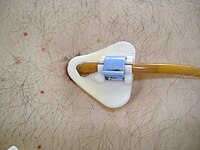
Useful traction technique for laparoscopic fundoplication without removing proceeding gastrostomy in a neurologically impaired patient with a body deformity
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Asian Journal of Endoscopic Surgery"
DOI: 10.1111/ases.13028
Abstract: Severely neurologically impaired patients often require the creation of a gastrostomy when they develop difficulty with oral intake followed by antireflux surgery. We use a traction technique for laparoscopic fundoplication without removing the gastrostomy in… read more here.
Keywords: without removing; fundoplication; traction; traction technique ... See more keywords

Mosapride for gastroesophageal reflux disease in neurologically impaired patients
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Pediatrics International"
DOI: 10.1111/ped.13144
Abstract: The prokinetic agent cisapride is effective for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in infants and children, but is no longer used for this purpose because of safety concerns. Therefore, other pharmacological agents need… read more here.
Keywords: mosapride gastroesophageal; neurologically impaired; reflux disease; gastroesophageal reflux ... See more keywords

Clinical presentations of erosive esophagitis found at endoscopy in neurologically impaired children: a historical study.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Annals of palliative medicine"
DOI: 10.21037/apm-22-783
Abstract: BACKGROUND Data is lacking as to the clinical presentation of erosive esophagitis (EE) in neurologically impaired children compared to non-neurologically impaired children (non-NIC). To determinate the clinical presentation, associations, management, and outcomes of EE in… read more here.
Keywords: erosive esophagitis; diagnosis; non neurologically; non nic ... See more keywords

Gastroesophageal Reflux in Neurologically Impaired Children: What Are the Risk Factors?
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Gut and Liver"
DOI: 10.5009/gnl16150
Abstract: Background/Aims Neurologically impaired patients frequently suffer from gastrointestinal tract problems, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In this study, we aimed to define the risk factors for GERD in neurologically impaired children. Methods From May… read more here.
Keywords: risk factors; neurologically impaired; reflux index; impaired children ... See more keywords

Effect of music listening on hypertonia in neurologically impaired patients—systematic review
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "PeerJ"
DOI: 10.7717/peerj.8228
Abstract: Background As music listening is able to induce self-perceived and physiological signs of relaxation, it might be an interesting tool to induce muscle relaxation in patients with hypertonia. To this date effective non-pharmacological rehabilitation strategies… read more here.
Keywords: music listening; effect; neurologically impaired; hypertonia neurologically ... See more keywords