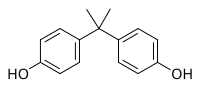
Sex-dependent effects of bisphenol A on type 1 diabetes development in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Archives of Toxicology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00204-018-2379-5
Abstract: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease caused by immune-mediated pancreatic β-cell destruction. The endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A (BPA) has widespread human exposure and can modulate immune function and the gut microbiome (GMB),… read more here.
Keywords: bpa; dependent effects; sex dependent; type diabetes ... See more keywords

Bisphenol A alteration of type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic (NOD) female mice is dependent on window of exposure
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Archives of Toxicology"
DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02419-4
Abstract: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease in which pancreatic β-cell destruction can be mediated by dysbiosis, infiltration of pro-inflammatory immune cells, and cytokines/chemokines. Exposure to bisphenol A (BPA), an endocrine disruptor (ED), can… read more here.
Keywords: diabetic nod; type diabetes; obese diabetic; non obese ... See more keywords

Empirical Dilation of Non-obstructive Dysphagia: Current Understanding and Future Directions
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Digestive Diseases and Sciences"
DOI: 10.1007/s10620-022-07451-6
Abstract: Non-obstructive dysphagia (NOD) is defined as symptomatic dysphagia in patients with negative endoscopic and radiographic workup. The management of NOD remains controversial as there is a discrepancy between different guidelines and clinical practice. Despite the… read more here.
Keywords: nod; dysphagia; dilation; empiric dilation ... See more keywords

Nodularin induced oxidative stress contributes to developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Ecotoxicology and environmental safety"
DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110444
Abstract: Nodularin (NOD) is a kind of cyanobacterial toxins. It is of concern due to elicit severe genotoxicity in humans and animals. The comprehensive evaluation of NOD-induced adverse effects in living organisms is urgently needed. This… read more here.
Keywords: zebrafish embryos; toxicity; nod; developmental toxicity ... See more keywords

Transgenic substitution with Greater Amberjack Seriola dumerili fish insulin 2 in NOD mice reduces beta cell immunogenicity
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40768-3
Abstract: Type I diabetes (T1D) is caused by immune-mediated destruction of pancreatic beta cells. This process is triggered, in part, by specific (aa 9–23) epitopes of the insulin Β chain. Previously, fish insulins were used clinically… read more here.
Keywords: insulin; nod; nod mice; seriola dumerili ... See more keywords

WDFY4 deficiency in NOD mice ameliorates autoimmune diabetes and insulitis.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America"
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2219956120
Abstract: The events that initiate autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice remain poorly understood. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are both required to develop disease, but their relative roles in initiating disease are unclear. To… read more here.
Keywords: nod mice; nod wdfy4; nod; mice ... See more keywords

IgM Immunotherapy Restores Immune Homeostasis and Reverses Hyperglycemia in New-Onset type 1 Diabetes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Transplantation"
DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000542593.93432.d0
Abstract: Goal To determine the mechanism by which IgM immunotherapy restores immune homeostasis in Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). Background IgM immunotherapy prevents the onset and progression of T1D. Methods 1) 5wks old non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice… read more here.
Keywords: igm immunotherapy; igm; mice; therapy ... See more keywords

Determination of the platinum-group elements and gold in ferromanganese nodule reference material NOD-A-1
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Geochemistry International"
DOI: 10.1134/s0016702917010037
Abstract: The concentrations of Ru, Pd, Ir, Pt, and Au were determined in a ferromanganese nodule reference sample NOD-A-1 by inductively coupled plasma mass-spectrometry. Sample preparation procedures include acid digestion and anion exchange preconcentration. Standard addition… read more here.
Keywords: reference; determination platinum; platinum group; ferromanganese nodule ... See more keywords

Comparison of biological features between severely immuno-deficient NOD/Shi-scid Il2rgnull and NOD/LtSz-scid Il2rgnull mice
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Experimental Animals"
DOI: 10.1538/expanim.19-0024
Abstract: Biological background data up to 11 weeks of age and tumorigenic susceptibility to xenotransplantation with HeLa cells were compared between severely immuno-deficient NOG and NSG mice. The body weight was lower in NOG mice than… read more here.
Keywords: nod; mice; severely immuno; nsg mice ... See more keywords

1726-P: MDA5, a Janus-Faced dsRNA Sensor in Coxsackievirus-Accelerated Autoimmune Diabetes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Diabetes"
DOI: 10.2337/db19-1726-p
Abstract: While microbial infections can trigger type 1 diabetes (T1D), innate immune activation and the synthesis of free radicals, proinflammatory cytokines, and type 1 interferons contribute to pancreatic β-cell destruction. We previously demonstrated that Coxsackievirus B3… read more here.
Keywords: autoimmune diabetes; mice; mda5; nod ... See more keywords

Pancreatic Alpha-Cells Contribute Together With Beta-Cells to CXCL10 Expression in Type 1 Diabetes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Frontiers in Endocrinology"
DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00630
Abstract: C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 (CXCL10) is a pro-inflammatory chemokine specifically recognized by the ligand receptor CXCR3 which is mostly expressed in T-lymphocytes. Although CXCL10 expression and secretion have been widely associated to pancreatic islets… read more here.
Keywords: cxcl10 expression; expression; mice; alpha cells ... See more keywords