
In vitro expression and functional characterization of NPA motifs in aquaporins of Nosema bombycis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Parasitology Research"
DOI: 10.1007/s00436-018-6044-y
Abstract: Nosema bombycis contains functional aquaporins (NbAQPs), which are key targets for exploring the mechanism of N. bombycis infection; however, the regulation of these NbAQPs remains unknown. The two highly conserved asparagine-proline-alanine sequences (NPA motifs) play… read more here.
Keywords: nosema bombycis; bombycis; npa motifs; nbaqp ... See more keywords

STING-dependent autophagy suppresses Nosema bombycis infection in silkworms, Bombyx mori.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Developmental and comparative immunology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103862
Abstract: Nosema bombycis is a unicellular spore-forming obligate parasite, related to fungi, and causes infections in economically important animals and are opportunistic human pathogens. However, the mechanisms of host response to N. bombycis remain unclear. STING… read more here.
Keywords: sting dependent; nosema bombycis; bombyx mori; bmsting 5bp ... See more keywords

Nosema bombycis microRNA-like RNA 8 (Nb-milR8) Increases Fungal Pathogenicity by Modulating BmPEX16 Gene Expression in Its Host, Bombyx mori
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Microbiology Spectrum"
DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01048-21
Abstract: A thorough understanding of fungal pathogen adaptations is essential for treating fungal infections. Recent studies have suggested that the role of small RNAs expressed in fungal microsporidia genomes are important for elucidating the mechanisms of… read more here.
Keywords: expression; microrna like; gene; bombycis ... See more keywords

Easy labeling of proliferative phase and sporogonic phase of microsporidia Nosema bombycis in host cells
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "PLoS ONE"
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179618
Abstract: Microsporidia are eukaryotic, unicellular parasites that have been studied for more than 150 years. These organisms are extraordinary in their ability to invade a wide range of hosts including vertebrates and invertebrates, such as human… read more here.
Keywords: phase; nosema bombycis; sporogonic phase; microsporidia nosema ... See more keywords

Identification and subcellular colocalization of protein transport protein Sec61α and Sec61γ in Nosema bombycis.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Gene"
DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.4097561
Abstract: The main function of Sec61 complex is participating in the transport of polypeptide chains across the endoplasmic reticulum. The Sec61α subunit is the largest subunit of the Sec61 complex and shows high degree of conservation.… read more here.
Keywords: nosema bombycis; transport; nbsec61 nbsec61; protein ... See more keywords

Detection and Characterization of Nosema bombycis Using TEM and SEM Techniques.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Archives of Razi Institute"
DOI: 10.22092/ari.2022.356482.1853
Abstract: Pebrine disease is the most important and dangerous disease of silkworm caused by Nosema bombycis as an obligate intracellular parasitic fungus. It has caused tremendous economic losses in the silk industry in recent years. Given… read more here.
Keywords: tem; disease; microscopy; pebrine disease ... See more keywords

Construction of scFv Antibodies against the Outer Loops of the Microsporidium Nosema bombycis ATP/ADP-Transporters and Selection of the Fragment Efficiently Inhibiting Parasite Growth
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "International Journal of Molecular Sciences"
DOI: 10.3390/ijms232315307
Abstract: Traditional sanitation practices remain the main strategy for controlling Bombyx mori infections caused by microsporidia Nosema bombycis. This actualizes the development of new approaches to increase the silkworm resistance to this parasite. Here, we constructed… read more here.
Keywords: outer loops; bombycis atp; growth; scfv ... See more keywords

Genome-Wide Characterization and Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Serpin Gene Family in Microsporidian Nosema bombycis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "International Journal of Molecular Sciences"
DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010550
Abstract: Microsporidia are ubiquitous in the environment, infecting almost all invertebrates, vertebrates, and some protists. The microsporidian Nosema bombycis causes silkworms pébrine disease and leads to huge economic losses. Parasite secreted proteins play vital roles in… read more here.
Keywords: serpin; comparative genomic; nosema; microsporidian nosema ... See more keywords

A Putative TRAPα Protein of Microsporidia Nosema bombycis Exhibits Non-Canonical Alternative Polyadenylation in Transcripts
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Journal of Fungi"
DOI: 10.3390/jof9040407
Abstract: Microsporidia are obligate intracellular eukaryotic parasites that have significantly reduced genomes and that have lost most of their introns. In the current study, we characterized a gene in microsporidia Nosema bombycis, annotated as TRAPα (HNbTRAPα).… read more here.
Keywords: alternative polyadenylation; microsporidia nosema; non canonical; nosema bombycis ... See more keywords
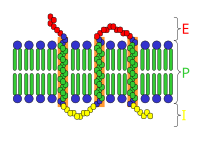
Identification and subcellular localization analysis of membrane protein Ycf 1 in the microsporidian Nosema bombycis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "PeerJ"
DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13530
Abstract: Microsporidia are obligate intracellular parasites that can infect a wide range of vertebrates and invertebrates including humans and insects, such as silkworm and bees. The microsporidium Nosema bombycis can cause pebrine in Bombyx mori, which… read more here.
Keywords: analysis; membrane protein; membrane; nosema bombycis ... See more keywords

A secretory hexokinase plays an active role in the proliferation of Nosema bombycis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "PeerJ"
DOI: 10.7717/peerj.5658
Abstract: The microsporidian Nosema bombycis is an obligate intracellular parasite of Bombyx mori, that lost its intact tricarboxylic acid cycle and mitochondria during evolution but retained its intact glycolysis pathway. N. bombycis hexokinase (NbHK) is not… read more here.
Keywords: hexokinase plays; nosema bombycis; plays active; bombycis ... See more keywords