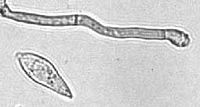
Appressorium-mediated plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae is regulated by a Pmk1-dependent hierarchical transcriptional network.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Nature microbiology"
DOI: 10.1038/s41564-021-00978-w
Abstract: Rice blast is a devastating disease caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae that threatens rice production around the world. The fungus produces a specialized infection cell, called the appressorium, that enables penetration through the… read more here.
Keywords: appressorium; plant; magnaporthe oryzae; pmk1 dependent ... See more keywords

The essential role of fungal peroxisomes in plant infection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Molecular Plant Pathology"
DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13180
Abstract: Abstract Several filamentous fungi are ecologically and economically important plant pathogens that infect a broad variety of crops. They cause high annual yield losses and contaminate seeds and fruits with mycotoxins. Not only powerful infection… read more here.
Keywords: essential role; fungal peroxisomes; plant infection; infection ... See more keywords

Dynamic expression of Ralstonia solanacearum virulence factors and metabolism-controlling genes during plant infection
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "BMC Genomics"
DOI: 10.1186/s12864-021-07457-w
Abstract: Background Ralstonia solanacearum is the causal agent of bacterial wilt, a devastating plant disease responsible for serious economic losses especially on potato, tomato, and other solanaceous plant species in temperate countries. In R. solanacearum ,… read more here.
Keywords: plant; virulence; infection; plant infection ... See more keywords

Identification of Aerotaxis Receptor Proteins Involved in Host Plant Infection by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci 6605
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Microbes and Environments"
DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.me21076
Abstract: Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci 6605 (Pta6605) is a foliar plant pathogen that causes wildfire disease on tobacco plants. It requires chemotaxis to enter plants and establish infection. While chemotactic signals appear to be the main… read more here.
Keywords: plant infection; aerotaxis; pta6605; host plant ... See more keywords