
Intravascular cells and circulating microparticles induce procoagulant activity via phosphatidylserine exposure in heart failure
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis"
DOI: 10.1007/s11239-019-01889-8
Abstract: Relatively little information is known about the definitive role of phosphatidylserine (PS) in the hypercoagulability of heart failure (HF). Our objectives were to assess the levels of PS exposure on microparticles (MPs) and blood cells… read more here.
Keywords: phosphatidylserine; procoagulant activity; heart failure;

Phosphatidylserine-mediated platelet clearance by endothelium decreases platelet aggregates and procoagulant activity in sepsis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04773-8
Abstract: The mechanisms that eliminate activated platelets in inflammation-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) in micro-capillary circulation are poorly understood. This study explored an alternate pathway for platelet disposal mediated by endothelial cells (ECs) through phosphatidylserine (PS)… read more here.
Keywords: sepsis; platelet clearance; procoagulant activity; clearance ... See more keywords

Direct Amplification of TF (Tissue Factor).
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology"
DOI: 10.1161/atvbaha.119.313215
Abstract: OBJECTIVE Regulation of TF (tissue factor):FVIIa (coagulation factor VIIa) complex procoagulant activity is especially critical in tissues where plasma can contact TF-expressing cells. One example is the liver, where hepatocytes are routinely exposed to plasma… read more here.
Keywords: fviia; procoagulant activity; activity; tissue factor ... See more keywords

Alterations to Sphingomyelin Metabolism Affect Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology"
DOI: 10.1161/atvbaha.122.318443
Abstract: Background: Our recent studies suggest that sphingomyelin levels in the plasma membrane influence TF (tissue factor) procoagulant activity. The current study was performed to investigate how alterations to sphingomyelin metabolic pathway would affect TF procoagulant… read more here.
Keywords: hemostasis; alterations sphingomyelin; activity; procoagulant activity ... See more keywords

MPs-ACT, an Assay to Evaluate the Procoagulant Activity of Microparticles
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis"
DOI: 10.1177/10760296231159374
Abstract: The procoagulant effect of microparticles (MPs) contributes to hypercoagulability-induced thrombosis. We provide preliminary findings of the MPs-Activated Clotting Time (MPs-ACT) assay to determine the procoagulant activity of MPs. MPs-rich plasma was obtained and recalcified. Changes… read more here.
Keywords: act assay; mps act; plasma; procoagulant activity ... See more keywords
High risk oral contraceptive hormones do not directly enhance endothelial cell procoagulant activity in vitro
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "PLOS ONE"
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284333
Abstract: Background Oral contraceptive (OC) use increases venous thromboembolism risk 2-5-fold. Procoagulant changes can be detected in plasma from OC users even without thrombosis, but cellular mechanisms that provoke thrombosis have not been identified. Endothelial cell… read more here.
Keywords: oral contraceptive; risk; activity; endothelial cell ... See more keywords

Temozolomide and Lomustine Induce Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Cancers"
DOI: 10.3390/cancers15082347
Abstract: Simple Summary Cancer patients, particularly with glioblastoma (GBM), are at increased risk for thrombosis. This risk is further increased upon treatment with chemotherapy. Tissue factor (TF) is the initiator of the extrinsic coagulation pathway and… read more here.
Keywords: tissue factor; expression; activity; gbm ... See more keywords
Procoagulant Activity in Amniotic Fluid Is Associated with Fetal-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Current Issues in Molecular Biology"
DOI: 10.3390/cimb44060185
Abstract: Procoagulant activity in amniotic fluid (AF) is positively correlated with phosphatidylserine (PS) and tissue factor (TF)-expressing(+) extracellular vesicles (EVs). However, it is unknown if pathological fetal conditions may affect the composition, phenotype, and procoagulant potency… read more here.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; activity amniotic; amniotic fluid; fetal derived ... See more keywords
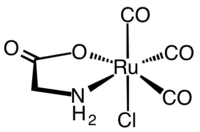
Ruthenium, Not Carbon Monoxide, Inhibits the Procoagulant Activity of Atheris, Echis, and Pseudonaja Venoms
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "International Journal of Molecular Sciences"
DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082970
Abstract: The demonstration that carbon monoxide releasing molecules (CORMs) affect experimental systems by the release of carbon monoxide, and not via the interaction of the inactivated CORM, has been an accepted paradigm for decades. However, it… read more here.
Keywords: echis pseudonaja; procoagulant activity; carbon monoxide; carbon ... See more keywords