
High amplitude and low frequency cyclic mechanical strain promotes degeneration of human nucleus pulposus cells via the NF‐κB p65 pathway
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of Cellular Physiology"
DOI: 10.1002/jcp.26551
Abstract: Disc degeneration alters the structure and function of intervertebral discs and is the basis of spinal degenerative diseases. To establish the molecular mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration caused by mechanical strain, this study examined the… read more here.
Keywords: human nucleus; cms; pulposus cells; pulposus ... See more keywords

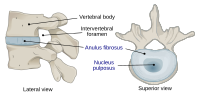
Notochordal and nucleus pulposus marker expression is maintained by sub-populations of adult human nucleus pulposus cells through aging and degeneration
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Scientific Reports"
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01567-w
Abstract: The nucleus pulposus (NP) of the intervertebral disc (IVD) demonstrates substantial changes in cell and matrix composition with both ageing and degeneration. While recent transcriptomic profiling studies have helped define human NP cell phenotype, it… read more here.
Keywords: adult human; marker; pulposus; expression ... See more keywords
HIF1A Alleviates compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived stem cells via upregulating autophagy.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Autophagy"
DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1872227
Abstract: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is the primary pathological mechanism that underlies low back pain. Overloading-induced cell death, especially endogenous stem cell death, is the leading factor that undermines intrinsic repair and aggravates IDD. Previous research… read more here.
Keywords: pulposus derived; pulposus; nucleus pulposus; stem ... See more keywords
MicroRNA-137 inhibits the inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human nucleus pulposus cells by targeting activin a receptor type I
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Bioengineered"
DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2042987
Abstract: ABSTRACT This study aimed to investigate the role played by microRNA (miR)-137 in intervertebral disc degeneration via targeting activin A receptor type I (ACVR1) and the underlying mechanism. Human nucleus pulposus cells were exposed to… read more here.
Keywords: pulposus; extracellular matrix; type; nucleus pulposus ... See more keywords

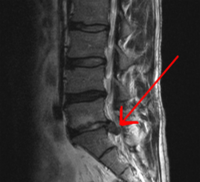
ACUTE NONCOMPRESSIVE NUCLEUS PULPOSUS EXTRUSION CAUSING PARAPLEGIA IN A SIBERIAN TIGER (PANTHERA TIGRIS ALTAICA)
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine"
DOI: 10.1638/2017-0079r1.1
Abstract: Abstract A neutered male Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica) presented with paraplegia of 5 days' duration. Thoracolumbar magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a focal, linear T2-W hyperintense intramedullary lesion at the level of T10–11 as… read more here.
Keywords: siberian tiger; pulposus; tigris altaica; panthera tigris ... See more keywords

Comparative metagenomic analysis of human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus and cartilaginous end plates
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine"
DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.927652
Abstract: Study design The diversity of microflora inhabiting endplate (EP) and nucleus pulposus (NP) tissues of human intervertebral disc (IVD) was profiled through NGS-supported 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Sixteen EP and their corresponding NP were excised… read more here.
Keywords: pulposus; abundance; ivd; human intervertebral ... See more keywords

Microtubule stabilization promotes the synthesis of type 2 collagen in nucleus pulposus cell by activating hippo-yap pathway
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Frontiers in Pharmacology"
DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1102318
Abstract: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is the cardinal pathological mechanism that underlies low back pain. Mechanical stress of the intervertebral disc may result in a change in nucleus pulposus cells state, matrix degradation, and degeneration of… read more here.
Keywords: pulposus; type collagen; stabilization promotes; microtubule stabilization ... See more keywords