
An evaluation of multiple algorithms for the measurement of the heart rate corrected JTpeak interval.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of electrocardiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2017.08.025
Abstract: Interest in the effects of drugs on the heart rate-corrected JTpeak (JTpc) interval from the body-surface ECG has spawned an increasing number of scientific investigations in the field of regulatory sciences, and more specifically in… read more here.
Keywords: heart rate; rate corrected; corrected jtpeak;

Sustained heart rate‐corrected QT prolongation during recovery from hypoglycaemia in people with type 1 diabetes, independently of recovery to hyperglycaemia or euglycaemia
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Diabetes"
DOI: 10.1111/dom.15005
Abstract: To investigate changes in cardiac repolarization abnormalities (heart rate‐corrected QT [QTc] [primary endpoint], T‐wave abnormalities) and heart‐rate variability measures in people with type 1 diabetes during insulin‐induced hypoglycaemia followed by recovery hyperglycaemia versus euglycaemia. read more here.
Keywords: people type; heart rate; rate corrected; recovery ... See more keywords
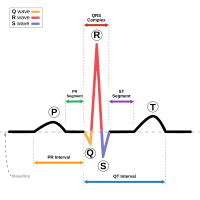
Association between heart rate-corrected QT interval and severe peripheral arterial disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and foot ulcers
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Endocrine Connections"
DOI: 10.1530/ec-21-0140
Abstract: Background A prolonged heart rate-corrected QT interval (QTc) has been associated with peripheral artery disease (PAD) in the general population. However, no study to date has identified a link between prolonged QTc and the severity… read more here.
Keywords: heart rate; rate corrected; severe pad; pad ... See more keywords

Interleukin-6 Elevation Is a Key Pathogenic Factor Underlying COVID-19-Associated Heart Rate-Corrected QT Interval Prolongation
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine"
DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.893681
Abstract: Background Heart rate-corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation is prevalent in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and is associated with poor outcomes. Recent evidence suggests that the exaggerated host immune-inflammatory response characterizing the disease,… read more here.
Keywords: prolongation; elevation; covid; rate corrected ... See more keywords

Heart-Rate-Corrected QT Interval Response to Ramosetron during Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A Randomized Trial
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of Personalized Medicine"
DOI: 10.3390/jpm12050811
Abstract: Ramosetron, often used to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting, might cause heart-rate-corrected (QTc) interval prolongation, as might robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP), which requires a steep Trendelenburg position and CO2 pneumoperitoneum. This study aimed to determine… read more here.
Keywords: laparoscopic prostatectomy; ramosetron; rate corrected; assisted laparoscopic ... See more keywords