
Structure-Relaxivity Relationships of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Advanced materials"
DOI: 10.1002/adma.201804567
Abstract: Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been extensively explored as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. With the increasing complexity in the structure of modern MNPs, the classical Solomon-Bloembergen-Morgan and the outer-sphere quantum mechanical theories established on… read more here.
Keywords: structure relaxivity; resonance imaging; magnetic resonance; magnetic nanoparticles ... See more keywords

A superparamagnetic polymersome with extremely high T2 relaxivity for MRI and cancer-targeted drug delivery.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Biomaterials"
DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.027
Abstract: Improving the relaxivity of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents is an important challenge for cancer theranostics. Herein we report the design, synthesis, characterization, theoretical analysis and in vivo tests of a superparamagnetic polymersome as a… read more here.
Keywords: high relaxivity; superparamagnetic polymersome; mri; extremely high ... See more keywords

Aqueous solutions of triblock copolymers used as the media affecting the magnetic relaxation properties of gadolinium ions trapped by metal-oxide nanostructures
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Journal of Molecular Liquids"
DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111821
Abstract: Abstract The present work introduces the optimization of the oxidative degradation, complex formation and aggregation of the water-soluble metal oxide nanostructures (the so-called keplerates) [{W6O21(H2O)5(OAc)0.5}12{Mo2O4(OAc)}30]48− (W72Mo60), [{Mo6O21(H2O)3(SO4)}12(VO)30(H2O)20]26− (Mo72V30), and [{Mo6O21}12Fe30(OAc)12{Mo2O7(H2O)}2{H2Mo2O8(H2O)}(H2O)91] (Mo72Fe30) in aqueous solutions containing… read more here.
Keywords: oxide nanostructures; aqueous solutions; metal oxide; h2o ... See more keywords

Binding modes of Fe(III) with graphene oxide in aqueous solutions. Competition with Sr2+, Cs+, Na+ ions and Fe(III) chelators
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Journal of Molecular Liquids"
DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112461
Abstract: Abstract The work is devoted to the analysis of the state of the Fe(III) ions in aqueous solutions of graphene oxide (GO) using NMR-relaxation method. The presence of graphene oxide in solution suppresses the hydrolysis… read more here.
Keywords: graphene oxide; iii graphene; modes iii; binding modes ... See more keywords

NMR characterizing mixed wettability under intermediate-wet condition.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Magnetic resonance imaging"
DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.09.023
Abstract: Applying the concept of effective relaxivity to characterize wettability is based on the configuration of fluid distributions in porous media. However, in mixed-wet porous media with intermediate-wet patches (homogeneous wetting region), effective surface relaxivity cannot… read more here.
Keywords: mixed wettability; surface relaxivity; intermediate wet; wettability ... See more keywords

Large Protein Assemblies for High-Relaxivity Contrast Agents: The Case of Gadolinium-Labeled Asparaginase
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Bioconjugate Chemistry"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00506
Abstract: Biologics are emerging as the most important class of drugs and are used to treat a large variety of pathologies. Most of biologics are proteins administered in large amounts, either by intramuscular injection or by… read more here.
Keywords: gadolinium; contrast; labeled asparaginase; relaxivity ... See more keywords

High Relaxivity with No Coordinated Waters: A Seemingly Paradoxical Behavior of [Gd(DOTP)]5- Embedded in Nanogels.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Inorganic chemistry"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c00225
Abstract: Nanogels (NGs) obtained by electrostatic interactions between chitosan and hyaluronic acid and comprising paramagnetic Gd chelates are gaining increasing attention for their potential application in magnetic resonance bioimaging. Herein, the macrocyclic complexes [Gd(DOTP)]5-, lacking metal-bound… read more here.
Keywords: relaxivity; relaxivity coordinated; high relaxivity; waters seemingly ... See more keywords
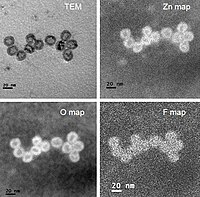
Structure-Relaxivity Mechanism of an Ultrasmall Ferrite Nanoparticle T1 MR Contrast Agent: The Impact of Dopants Controlled Crystalline Core and Surface Disordered Shell.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Nano letters"
DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04574
Abstract: Ultrasmall ferrite nanoparticles (UFNPs) have emerged as powerful magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1 nanoprobe for noninvasive visualization of biological events. However, the structure-relaxivity relationship and regulatory mechanism of UFNPs remain elusive. Herein, we developed chemically… read more here.
Keywords: structure relaxivity; crystalline core; ultrasmall ferrite; shell ... See more keywords

Gd-Dots with Strong Ligand-Water Interaction for Ultrasensitive Magnetic Resonance Renography.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "ACS nano"
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07959
Abstract: Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents with both significantly enhanced relaxivity and minimal safety risk are of great importance for sensitive clinical diagnosis, but have rarely been reported. Herein, we present a simple strategy to improve… read more here.
Keywords: water; magnetic resonance; renography; interaction ... See more keywords

Relaxivity and toxicological properties of manganese oxide nanoparticles for MRI applications.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "RSC advances"
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra04421b
Abstract: Manganese oxide nanoparticles (MONs) have received growing attention as alternative T 1 MRI contrast agents due to the association of commercial gadolinium-based contrast agents with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Since the seminal publication first describing the… read more here.
Keywords: relaxivity; toxicological properties; manganese oxide; contrast agents ... See more keywords

Rigid versions of PDTA4- incorporating a 1,3-diaminocyclobutyl spacer for Mn2+ complexation: stability, water exchange dynamics and relaxivity.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Dalton transactions"
DOI: 10.1039/d1dt02498a
Abstract: Rigid derivatives of the acyclic ligand PDTA4- (H4PDTA = propylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid) were prepared by functionalization of a 1,3-diaminocyclobutyl spacer. The new ligands contain either four acetate groups attached to the central scaffold (H4L1) or incorporate… read more here.
Keywords: coordinate species; water; diaminocyclobutyl spacer; relaxivity ... See more keywords