
Boron isotopic signatures of melt inclusions from North Iceland reveal recycled material in the Icelandic mantle source
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta"
DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.11.013
Abstract: Trace element and volatile heterogeneity in the Earth's mantle is in uenced by the recycling of oceanic lithosphere through subduction. Oceanic island basalts commonly have high concentrations of volatiles compared to mid-ocean ridge basalts, but the… read more here.
Keywords: reykjanes ridge; mantle; x11b; melt inclusions ... See more keywords

Selenium and tellurium in Reykjanes Ridge and Icelandic basalts: Evidence for degassing-induced Se isotope fractionation
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta"
DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.07.029
Abstract: Abstract Selenium behaves as a chalcophile and moderately volatile element during planetary accretion and magmatic processes on Earth. Together with the geochemically similar S and Te, Se is more volatile than most other moderately volatile… read more here.
Keywords: induced isotope; degassing induced; isotope fractionation; reykjanes ridge ... See more keywords
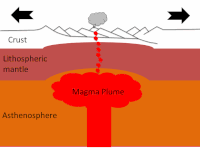
Volcanism and hydrothermalism on a hotspot–influenced ridge: Comparing Reykjanes Peninsula and Reykjanes Ridge, Iceland
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2017.10.017
Abstract: Abstract Current estimates indicate that the number of high-temperature vents (one of the primary pathways for the heat extraction from the Earth's mantle) – at least 1 per 100 km of axial length – scales with… read more here.
Keywords: reykjanes ridge; high temperature; reykjanes peninsula; ridge ... See more keywords

Subarctic Front migration at the Reykjanes Ridge during the mid‐ to late Holocene: evidence from planktic foraminifera
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Boreas"
DOI: 10.1111/bor.12263
Abstract: Expansion of fresh and sea-ice loaded surface waters from the Arctic Ocean into the sub-polar North Atlantic is suggested to modulate the northward heat transport within the North Atlantic Current (NAC). The Reykjanes Ridge south… read more here.
Keywords: reykjanes ridge; late holocene; surface; mid late ... See more keywords