
The Rhodococcus equi virulence protein VapA disrupts endolysosome function and stimulates lysosome biogenesis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "MicrobiologyOpen"
DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.416
Abstract: Rhodococcus equi (R. equi) is an important pulmonary pathogen in foals that often leads to the death of the horse. The bacterium harbors a virulence plasmid that encodes numerous virulence‐associated proteins (Vaps) including VapA that… read more here.
Keywords: virulence; rhodococcus equi; lysosome biogenesis; function ... See more keywords

Immune Reconstitution Syndrome secondary to Rhodococcus equi infection in a patient with HIV and Burkitt's lymphoma.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of infection and public health"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2016.05.001
Abstract: Immune Reconstitution Syndrome (IRIS) has been associated with a variety of infections in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). However, we are reporting the first case of IRIS secondary to Rhodococcus equi (R. equi) in… read more here.
Keywords: hiv; infection; rhodococcus equi; secondary rhodococcus ... See more keywords

Rhodococcus equi infection as inaugural manifestation of idiopathic CD4+ lymphopenia: A rare entity and a therapeutic challenge.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2020 at "Pulmonology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.06.002
Abstract: We report a case of disseminated infection by Rhodococcus equi as the inaugural manifestation of idiopathic T-CD4+ lymphopenia. We aim to demonstrate our diagnostic and therapeutic approach and focus on the major dilemmas arising from… read more here.
Keywords: idiopathic cd4; manifestation idiopathic; infection; rhodococcus equi ... See more keywords

Guinea pig infection with the intracellular pathogen Rhodococcus equi.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Veterinary microbiology"
DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.11.019
Abstract: Rhodococcus equi is an opportunistic, intracellular pathogen that causes pyogranulomatous pneumonia in foals and immunocompromised people. Currently, there is no experimental model of R. equi pneumonia other than intra-bronchial experimental infection of foals with R.… read more here.
Keywords: guinea; guinea pig; infection; rhodococcus equi ... See more keywords

Virulence‐associated protein A from Rhodococcus equi is an intercompartmental pH‐neutralising virulence factor
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Cellular Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12958
Abstract: Professional phagocytic cells such as macrophages are a central part of innate immune defence. They ingest microorganisms into membrane‐bound compartments (phagosomes), which acidify and eventually fuse with lysosomes, exposing their contents to a microbicidal environment.… read more here.
Keywords: associated protein; virulence associated; virulence factor; virulence ... See more keywords

Rhodococcus equi Foal Pneumonia: Update on Epidemiology, Immunity, Treatment, and Prevention.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Equine veterinary journal"
DOI: 10.1111/evj.13567
Abstract: Pneumonia in foals caused by the bacterium Rhodococcus equi has a worldwide distribution and is a common cause of disease and death for foals. The purpose of this narrative review is to summarise recent developments… read more here.
Keywords: rhodococcus equi; pneumonia; treatment prevention; equi pneumonia ... See more keywords

Fecal concentration of Rhodococcus equi determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction of rectal swab samples to differentiate foals with pneumonia from healthy foals
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine"
DOI: 10.1111/jvim.16438
Abstract: Abstract Background Diagnostic accuracy of real‐time, quantitative PCR (qPCR) assays to quantify virulent Rhodococcus equi using rectal swab samples has not been systematically evaluated. Objective To evaluate the accuracy of qPCR of rectal swab samples… read more here.
Keywords: healthy foals; swab samples; rhodococcus equi; rectal swab ... See more keywords

Virulence plasmids in clinical isolates of Rhodococcus equi from sick foals in the Netherlands
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Letters in Applied Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1111/lam.13769
Abstract: Clinical samples from 123 foals with suspected rhodococcosis submitted to the Veterinary Microbiological Diagnostic Centre of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine between 1993 and 2006 were tested for the presence of the virulence gene vapA.… read more here.
Keywords: clinical isolates; rhodococcus equi; plasmids clinical; plasmid ... See more keywords
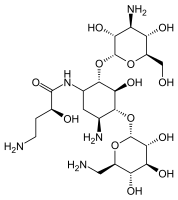
Antimicrobial Resistance Spectrum Conferred by pRErm46 of Emerging Macrolide (Multidrug)-Resistant Rhodococcus equi
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Journal of Clinical Microbiology"
DOI: 10.1128/jcm.01149-21
Abstract: Clonal multidrug resistance recently emerged in Rhodococcus equi, complicating the therapeutic management of this difficult-to-treat animal- and human-pathogenic actinomycete. The currently spreading multidrug-resistant (MDR) “2287” clone arose in equine farms upon acquisition, and coselection by… read more here.
Keywords: multidrug resistant; multidrug; rhodococcus equi; resistance ... See more keywords

Differential Effects of Rhodococcus equi Virulence-Associated Proteins on Macrophages and Artificial Lipid Membranes
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Microbiology Spectrum"
DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03417-22
Abstract: Rhodococcus equi is a major cause of life-threatening pneumonia in foals and occasionally in immunocompromised persons. Virulence-associated protein A (VapA) promotes R. equi multiplication in lung macrophages, which are the major host cells during foal… read more here.
Keywords: rhodococcus equi; vapa; multiplication; virulence ... See more keywords

Treatment and prevention of Rhodococcus equi in foals
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Veterinary Record"
DOI: 10.1136/vr.l4505
Abstract: Rhodococcus equi is an intracellular, facultative, Gram-positive coccobacillus that is ubiquitous in soil. It is also one of the most common causes of pneumonia in foals and has a major financial impact on the horse… read more here.
Keywords: treatment prevention; rhodococcus equi; equi foals; equi ... See more keywords