
Sedentary work and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2021 at "Journal of Occupational Health"
DOI: 10.1002/1348-9585.12239
Abstract: Abstract Objectives This systematic review and meta‐analysis aimed to assess sedentary work's contribution to breast cancer risk quantitatively using thorough research articles. Methods We performed a meta‐analysis using a registered protocol in PROSPERO (registration number:… read more here.
Keywords: work; risk; sedentary work; analysis ... See more keywords

Long working hours, sedentary work, noise, night shifts and risk of ischaemic heart disease
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Heart"
DOI: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-320999
Abstract: Objective Ischaemic heart disease (IHD) is a leading cause of death in Western countries. The aim of this study was to examine the associations between occupational exposure to loud noise, long working hours, shift work,… read more here.
Keywords: working hours; sedentary work; noise night; night ... See more keywords
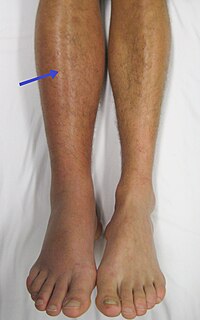
0171 Sedentary work and risk of venous thromboembolism
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Occupational and Environmental Medicine"
DOI: 10.1136/oemed-2017-104636.138
Abstract: Objective Prolonged seated immobility during long-distance flights is related to an increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) but little is known on the risk, if any, related to sedentary work. The objective of this paper… read more here.
Keywords: risk venous; work; risk; sedentary work ... See more keywords

The Effect of Physiotherapy Interventions in the Workplace through Active Micro-Break Activities for Employees with Standing and Sedentary Work
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Healthcare"
DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10102073
Abstract: Workers worldwide experience a range of occupational musculoskeletal disorders that affect both the functionality of many parts of their body and their overall performance. Physiotherapists provide counseling and treatment programs during work. Recently, physiotherapy interventions… read more here.
Keywords: sedentary work; physiotherapy interventions; active micro; micro ... See more keywords

Consequences of prolonged sedentary work during the COVID-19 pandemic
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics"
DOI: 10.37190/abb-02210-2023-02
Abstract: Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic has reduced physical activity and increased the time spent sitting. Combined with the lack of ergonomics at home workplaces, the risk of discomfort has increased, especially around the cervical spine and… read more here.
Keywords: prolonged sedentary; sedentary work; cervical spine; covid ... See more keywords