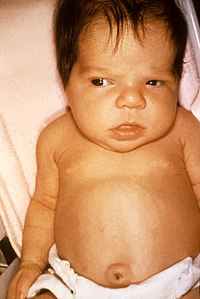
Biallelic mutations in TTC26 (IFT56) cause severe biliary ciliopathy in humans.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Hepatology"
DOI: 10.1002/hep.30982
Abstract: The clinical consequences of defective primary cilium (ciliopathies) are characterized by marked phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity. Although fibrocystic liver disease is an established ciliopathy phenotype, severe neonatal cholestasis is rarely recognized as such. We describe… read more here.
Keywords: severe neonatal; cause; neonatal cholestasis; ttc26 ift56 ... See more keywords

Survival Without Severe Neonatal Morbidity in Very Preterm Twins According to Planned Mode of Delivery.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Obstetrics and gynecology"
DOI: 10.1097/aog.0000000000004639
Abstract: OBJECTIVE To assess survival to discharge without severe neonatal morbidity by planned mode of delivery for twins born before 32 weeks of gestation. METHODS The JUMODA (JUmeaux MODe d'Accouchement) study was a French national prospective,… read more here.
Keywords: survival; neonatal morbidity; delivery; without severe ... See more keywords

Severe neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia: lessons learnt from a national perinatal audit
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Archives of Disease in Childhood"
DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2021-322891
Abstract: Objectives To describe characteristics of neonates with severe neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia (SNH) and to gain more insight in improvable factors that may have contributed to the development of SNH. Design and setting Descriptive study, based on… read more here.
Keywords: perinatal audit; hyperbilirubinaemia; neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia; improvable factors ... See more keywords

Clinical evaluation of severe neonatal Hyperbilirubinaemia in a resource-limited setting: a 4-year longitudinal study in south-East Nigeria
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "BMC Pediatrics"
DOI: 10.1186/s12887-018-1174-z
Abstract: BackgroundNeonatal hyperbilirubinaemia is one of the commonest causes of hospital visit in the neonatal period. When severe, it is a leading cause of irreversible neurological and musculoskeletal disability. Prompt recognition and timely interventions are imperative… read more here.
Keywords: severe neonatal; severe hyperbilirubinaemia; year; hyperbilirubinaemia ... See more keywords

Severe Neonatal Interstitial Lung Disease Caused by a Rare Surfactant Protein C Mutation.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Pediatrics"
DOI: 10.1542/peds.2022-060038
Abstract: Childhood interstitial lung disease (chILD) is a collective term for a group of rare lung disorders of heterogeneous origin. Surfactant dysfunction disorders are a cause of chILD with onset during the neonatal period and infancy.… read more here.
Keywords: neonatal interstitial; lung; lung disease; interstitial lung ... See more keywords

A Novel Homozygous PKP2 Variant in Severe Neonatal Non-compaction and Concomitant Ventricular Septal Defect: A Case Report
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2022 at "Frontiers in Pediatrics"
DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.801491
Abstract: Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare and genetically heterogeneous cardiomyopathy. The disorder vastly affects infants and young children. Severe neonatal LVNC is relatively rare. The prevalence of genetic defects underlying pediatric and adult-onset LVNC… read more here.
Keywords: novel homozygous; pkp2 variant; homozygous pkp2; non compaction ... See more keywords

[Severe neonatal anemia due to fetomaternal hemorrhage: an ilustrative case].
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Archivos argentinos de pediatria"
DOI: 10.5546/aap.2019.e142
Abstract: Fetomaternal transfusion (FMT) is defined by the transfer of fetal blood into the maternal circulation. The incidence of massive FMT is estimated to be approximately 0.2-0.9 % of births. Although a number of etiologies have… read more here.
Keywords: neonatal anemia; severe neonatal; anemia; anemia due ... See more keywords