
Duration of moderate to vigorous daily activity is negatively associated with slow walking speed independently from step counts in elderly women aged 75 years or over: A cross-sectional study.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2018 at "Archives of gerontology and geriatrics"
DOI: 10.1016/j.archger.2017.10.003
Abstract: OBJECTIVES This study aimed 1) to examine whether objectively measured duration of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) was associated with slow walking speed, independent from step counts, in elderly women aged 75 or over… read more here.
Keywords: slow walking; duration; speed; associated slow ... See more keywords
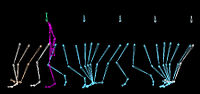
An effective balancing response to lateral perturbations at pelvis level during slow walking requires control in all three planes of motion.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2017 at "Journal of biomechanics"
DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2017.06.020
Abstract: In this study we investigated balancing responses to lateral perturbations during slow walking (0.85m/s). A group of seven healthy individuals walked on an instrumented treadmill while being perturbed at the level of waist at left… read more here.
Keywords: slow walking; lateral perturbations; step; walking requires ... See more keywords

Fast and slow walking driven by chemical fuel.
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2023 at "Chemical communications"
DOI: 10.1039/d3cc00357d
Abstract: We demonstrate the fast forward and slow backward motion of a biped on a tetrahedral track using chemical fuel, cooperative binding and kinetic selectivity. Walking of the biped is based on its dibenzyl amine feet… read more here.
Keywords: driven chemical; fuel; fast slow; slow walking ... See more keywords

Motoric Cognitive Risk Syndrome: Could It Be Defined Through Increased Five-Times-Sit-to-Stand Test Time, Rather Than Slow Walking Speed?
Sign Up to like & getrecommendations! Published in 2019 at "Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience"
DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00434
Abstract: Background: Slow walking speed, time to perform the five-times-sit-to-stand (FTSS) test and motoric cognitive risk syndrome (MCR; defined as slow gait speed combined with subjective cognitive complaint) have been separately used to screen older individuals… read more here.
Keywords: slow walking; risk; time; mci ... See more keywords